2008 Democratic Party presidential primaries

| ||||||||||||||||||||||
4,233 delegates to the Democratic National Convention 2,117 (majority) votes needed to win | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Democratic Party | |
|---|---|
| Republican Party | |
| Minor parties | |
| Related races | |
| |
| ||
|---|---|---|
|
Personal
Illinois State Senator and U.S. Senator from Illinois 44th President of the United States
Tenure
 |
||
| ||
|---|---|---|
|
First Lady of the United States
U.S. Senator from New York
U.S. Secretary of State
2008 presidential campaign 2016 presidential campaign Organizations
|
||
| ||
|---|---|---|
|
Personal U.S. Senator from Delaware 47th Vice President of the United States Vice presidential campaigns 46th President of the United States Incumbent Tenure  |
||
From January 3 to June 3, 2008, voters of the Democratic Party chose their nominee for president in the 2008 United States presidential election. Senator Barack Obama of Illinois was selected as the nominee, becoming the first African American to secure the presidential nomination of any major political party in the United States. However, due to a close race between Obama and Senator Hillary Clinton of New York, the contest remained competitive for longer than expected; neither candidate received enough pledged delegates from state primaries and caucuses to achieve a majority, without endorsements from unpledged delegates (superdelegates).

The presidential primaries actually consisted of both primary elections and caucuses, depending upon what the individual state chose. The goal of the process was to elect the majority of the 4,233 delegates to the 2008 Democratic National Convention, which was held from Monday, August 25, through Thursday, August 28, 2008, in Denver, Colorado. To secure the nomination, a candidate needed to receive at least 2,117 votes at the convention—or a simple majority of the 4,233 delegate votes. This total included half-votes from American Samoa, Guam, the United States Virgin Islands, in addition to Democrats Abroad, as well as 'superdelegates'—party leaders and elected officials who were not chosen through a primary or caucus. The race was further complicated by a controversy over the scheduling of the Michigan and Florida state primaries, which had been scheduled earlier than party rules permitted, affecting the number of delegates that those states sent to the national convention.

The popular vote tally from most news organizations did not include the states of Iowa, Maine, Nevada and Washington, as these states did not release the results of the popular vote from their caucuses. The media reports did include Florida, which neither Clinton nor Obama contested, as well as Michigan. Both states were penalized by the Democratic National Committee (DNC) for violating party rules. Michigan proved a source of controversy due to the change in the date of the primary election. Consequently, Obama and other candidates removed their names from the ballot yet Clinton did not. The DNC did not count the popular vote from Michigan, and evenly split the state's delegates between Clinton and Obama. As a result, without the Michigan vote, Obama won the popular vote; whereas with the votes from Michigan, Clinton won the popular vote.[3] Nevertheless, regardless of how votes were counted, the candidates' totals were within less than one percent of each other.[4]

Obama received enough superdelegate endorsements on June 3 to claim that he had secured the simple majority of delegates necessary to win the nomination, before Clinton conceded the nomination four days later.[5][6] Obama was nominated on the first ballot, at the August convention. He went on to win the general election, and became the 44th president of the United States on January 20, 2009. Clinton went on to serve as Obama's Secretary of State for his first term as president, and the Democratic nominee for president in 2016, losing to Donald Trump.

These primaries included the nominees for the next three elections- Obama again in 2012, Clinton in 2016, and Biden in 2020.

Candidates and results
Notes for the following table:

- Delegate counts:
- The pledged delegate estimates come from the sum of the Current estimate columns for the states listed in the Chronicle section later in this article
- The source for superdelegate estimates is the 2008 Democratic Convention Watch blog. Superdelegate endorsements were frozen on June 7, the date of Clinton's concession speech.[7]
- Ordering:
Nominee
| Candidate | Most recent office held at the end of the primaries |
Home State | Pledged delegate vote estimate[8] |
Superdelegate vote estimate[7] |
Total delegate vote estimate |
Campaign status | Running mate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Barack Obama |
U.S. Senator from Illinois (2005–2008) |
1,794½ 51% |
478 66% |
2,272½ 53% |
 (Campaign) Secured nomination: June 3, 2008 |
Joe Biden | ||
Withdrew during the primaries
| Candidate | Most recent office held at the end of the primaries |
Home State | Pledged delegate vote estimate[8] |
Superdelegate vote estimate[7] |
Total delegate vote estimate |
Campaign status | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Hillary Clinton |
U.S. Senator from New York (2001–2009) |
1,731½ 49% |
246½ 34% |
1,978 46% |
 (Campaign) (Endorsed Obama, later became Secretary of State)[9] | ||
 John Edwards |
U.S. Senator from North Carolina (1999–2005) |
14½ <1% |
0 |
14½ 1% |
(Campaign) Withdrew: January 30, 2008 (Endorsed Obama)[10] | ||
 Joe Biden |
U.S. Senator from Delaware (1973–2009) |
0 | 0 | 0 |  (Campaign) Withdrew: January 3, 2008 (Endorsed Obama, who later chose Biden as his vice presidential running mate) | ||
 Bill Richardson |
Governor of New Mexico (2003–2011) |
0 | 0 | 0 |  (Campaign) Withdrew: January 10, 2008 (Endorsed Obama) | ||
 Evan Bayh |
U.S. Senator from Indiana (1999–2011) |
0 | 0 | 0 |  (Campaign) Withdrew: December 16, 2006 (Endorsed Clinton, then Obama) | ||
 Chris Dodd |
U.S. Senator from Connecticut (1981–2011) |
0 | 0 | 0 |  (Campaign) Withdrew: January 3, 2008 (Endorsed Obama) | ||
 Mike Gravel |
U.S. Senator from Alaska (1969–1981) |
0 | 0 | 0 | (Campaign) Withdrew: March 26, 2008 (Endorsed Jesse Johnson for Libertarian nomination) | ||
 Dennis Kucinich |
U.S. Representative for Ohio's 10th (1997–2013) |
0 | 0 | 0 |  (Campaign) Withdrew: January 23, 2008 (Endorsed Obama) | ||
 Tom Vilsack |
Governor of Iowa
(1999–2007) |
0 | 0 | 0 |  (Campaign) Withdrew: February 23, 2007 (Endorsed Clinton) | ||
Declined to run
- Wesley Clark, former commander of NATO and presidential candidate in 2004.
- Tom Daschle, former U.S. senator of South Dakota.
- Howard Dean, former governor of Vermont and chair of the Democratic National Committee.
- Russ Feingold, U.S. senator of Wisconsin.
- Al Gore, former Vice President of the United States and the Democratic presidential nominee in 2000.
- John Kerry, U.S. senator of Massachusetts and the Democratic presidential nominee in 2004.
- Al Sharpton, civil rights activist and candidate for the U.S. Senate in 1992 and 1994.
- Mark Warner, former governor of Virginia.
Delegate system
Delegates are the people who decided the nomination at the Democratic National Convention. Delegates from fifty US states, the District of Columbia, and Puerto Rico had a single vote each, while delegates from American Samoa, the Virgin Islands, Guam and Democrats Abroad, as well as the states of Florida and Michigan, which contravened the schedule, had half a vote each. Thus, the total number of delegates was slightly higher than the total number of available delegate votes (4,049).[11] This is now updated to 4,233 with FL-MI delegations.

Pledged delegates
In the modern presidential primary system, candidates for the nomination campaign in a series of primary elections and caucus events. For the Democratic Party, the results from these primaries and caucuses determine the number of pledged delegates committed to vote for each candidate at the Democratic National Convention, intended to reflect the will of the voters. These delegates are not legally bound to vote for the candidate they represent, but candidates may remove delegates whom they feel may be disloyal, and delegates generally vote as pledged.[12] Under the party's Delegate Selection Rules for the 2008 Democratic National Convention, delegates were allocated to each of the fifty U.S. states according to two main criteria: the proportion of votes each state had given to the Democratic candidate in the previous three presidential elections, and the percentage of votes each state had in the United States Electoral College. In addition, fixed numbers of delegates were allocated to the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico, American Samoa, Guam, the U.S. Virgin Islands, and Democrats Abroad.[13] In 2008, a total of 3,253 pledged delegate votes would be awarded through the primaries and caucuses.

Superdelegates
Superdelegate votes are given equal weight to the votes of pledged delegates. Superdelegates are members of the United States House of Representatives and Senate, state and territorial governors, members of the Democratic National Committee, distinguished party leaders, and add-on delegates selected by the state parties. They represented almost 20 percent of the total 4,233 delegates.

The number and composition of superdelegates had the potential to change right up to the start of the Democratic National Convention. The total number of superdelegate votes at the start of the primary season in October 2007 stood at 850. Various events such as deaths, elections, and disqualifications may alter the final number of superdelegates voting in the primary.

While officially uncommitted until the convention, the superdelegates may publicly endorse or commit to a candidate at any time. The presidential candidates compete heavily for these commitments. News organizations survey the superdelegates periodically throughout the election season and try to calculate how many have committed to each of the candidates. The media often include these superdelegate estimates in their reporting on the race, leading to differing delegate counts from various news sources.

Delegate selection rules

Under the Democratic Party's Delegate Selection Rules for the 2008 Democratic National Convention,[13] delegates are awarded by proportional representation, with a minimum 15 percent threshold required to receive delegates. Each state party is required to publish its own state level delegate selection plan, indicating how the state will select delegates at the congressional and statewide level, how the delegation will implement the party's affirmative action policy, and how the delegation will ensure an equal balance between women and men. Those plans were adopted at state conventions and forwarded to the national party in mid-2007.

In most state caucuses, the viability threshold must be met at each level in the process, from the precinct level upwards. This puts enormous pressure on the remaining candidates to gain the support of voters whose chosen candidates fall below the 15 percent mark.[14] The focus on viability is designed to weed out small, divisive factions from gaining delegates to disrupt the national convention. However, this can result in candidates gaining viability in some precincts but not in others, and a complicated "caucus math" is required to allocate delegates to the county and state conventions for each precinct.[15] In the primaries, the viability threshold is set based on statewide and congressional district votes. At-large and PLEO (Party Leaders and Elected Officials) delegates are allocated based on statewide votes, while district-level delegates are allocated by district votes.[13]

Opinion polling


Campaign
Notes for the tables in this section:

- Votes to the Convention column:
- The source for delegation sizes is the Democratic National Committee's official Call for the 2008 Democratic National Convention.[16] Specific sources are present for Florida and Michigan. Very recent changes not already in the official source are indicated by the footnotes.
- Pledged Delegate Votes Estimate column:
- The source is each state's primary or caucus article. Click on the Specific Election (link) column to see the sources used in those articles.
- The candidate with the highest pledged delegate vote is highlighted. In some cases, this may be different from the winner of the popular vote.
Early campaigning

The earliest significant candidate to launch their candidacy was Mike Gravel in April 2006. However, for the most part, the race for the 2008 presidential nomination did not truly begin in earnest until after the 2006 midterm elections. Between November 2006 and February 2007, nine major candidates opened their campaigns: Evan Bayh as an exploratory committee, Joe Biden, Hillary Clinton, Chris Dodd, John Edwards, Dennis Kucinich, Barack Obama, Bill Richardson, and Tom Vilsack. Potential candidates John Kerry, Al Gore, Russ Feingold, Tom Daschle, Wesley Clark, Sam Nunn, Mark Warner, and Al Sharpton reportedly considered running but ultimately declined to seek the nomination. Bayh said he would not seek the nomination on December 16, 2006, and withdrew from the race. Soon Vilsack dropped out in February 2007.

During the first three months of 2007, Clinton and Obama raised over $20 million each, while Edwards raised more than $12 million.[17] The three candidates quickly became the frontrunners for the nomination,[18] a status they held all the way through the end of 2007.

On November 21, Obama announced that Oprah Winfrey would be campaigning for him in the early primary states,[19] setting off speculation that, although celebrity endorsements typically have little effect on voter opinions, Winfrey's participation would supply Obama with a large, receptive audience.[20] As word spread that Oprah's first appearance would be in Iowa, polls released in early December revealed that Obama had taken the lead in that decisive state.[21] Then, on December 8, Oprah kicked off a three-state tour supporting Obama's campaign,[22] where she drew record-setting crowds in Iowa, New Hampshire,[23] and South Carolina, and was described as "more cogent, more effective, more convincing" than anyone on the campaign trail.[24] The Oprah-Obama tour dominated political news headlines[25] and cast doubts over Clinton's ability to recover her recently-lost lead in Iowa caucus polls.[26] A poll released less than two weeks after Winfrey campaigned found that Obama had achieved more popularity in Iowa than ever recorded before.[27]

At year's end, on December 31, Clinton held a substantial lead in superdelegates, and she was leading in the national polls with 42% of likely voters, over Obama with 23%, and Edwards with 16%.[28] However, Edwards and Obama remained close in state polls for the early contests, including the Iowa caucuses, where the final polling average had Obama leading narrowly with 31%, over Clinton with 30%, Edwards with 26%, Biden with 5%, and Richardson also with 5%.[29]

January 2008
Following tradition, the 2008 primary calendar began with the Iowa caucuses and the New Hampshire primary. The Nevada caucuses and the South Carolina primary were the third and fourth contests sanctioned by the Democratic National Committee. Under the national committee's rules, no state was allowed to hold primaries or caucuses before February 5 with the exceptions of these four states.[30] Michigan and Florida also held early primaries. However, as the contests were unsanctioned, the results were not recognized by the national committee until a compromise was reached four months later.[2]

The following table shows the pledged delegate votes awarded in the first four contests recognized by the DNC.

| Details | Delegate votes to the convention | Pledged delegate vote count[31] | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Election result | Change notes |
Final estimate | |||||||||
| Date | Election link | Pledged | Super | Total | Obama | Clinton | Edwards | Obama | Clinton | Edwards | |
| January 3 | Iowa caucuses | 45 | 12 | 57 | 16 | 15 | 14 | [32][33] | 28 | 14 | 3 |
| January 8 | New Hampshire primary | 22 | 8 | 30 | 9 | 9 | 4 | [34] | 13 | 9 | 0 |
| January 19 | Nevada caucuses | 25 | 9 | 34 | 13 | 12 | 0 | [35] | 14 | 11 | 0 |
| January 26 | South Carolina primary | 45 | 9 | 54 | 25 | 12 | 8 | [36] | 33 | 12 | 0 |
| – | Total | 137 | 38 | 175 | 63 | 48 | 26 | 88 | 46 | 3 | |
Obama won the Iowa caucuses with 38% of the vote, over Edwards with 30% and Clinton with 29%. His victory brought him to national prominence as many voters tuned into the race for the first time. In a speech given that evening, he defined the word "change" as the primary theme of his campaign and said, "On this January night, at this defining moment in history, you have done what the cynics said we couldn't do."[37] The delegate count was virtually tied, but Clinton's surprising third-place finish in the popular vote damaged her image as being the "inevitable" nominee.[38] However, she remained upbeat, saying "This race begins tonight and ends when Democrats throughout America have their say. Our campaign was built for a marathon."[38] The following day, reports described "panic" among some Clinton donors,[39] and rumors of a staff shake-up began to circulate.[40] Biden and Dodd both withdrew from the race.


After Obama's upset win in the Iowa caucuses, it appeared to many political observers that he would ride a wave of momentum through the New Hampshire primary and then go on to win the Democratic nomination. Eulogies were published on the Clinton campaign,[41] as Obama surged to a roughly 10-point lead in the New Hampshire polls.[42] However, the race turned quickly in the days before the primary, and the polls were slow to register a reversal toward Clinton. At the Saint Anselm College New Hampshire debate on January 5, 2008, Edwards sided with Obama against Clinton.[43] In one noted exchange, Edwards said that Clinton could not bring about change, while he and Obama could, saying "Any time you speak out powerfully for change, the forces for status quo attack." Clinton passionately retorted, saying, "Making change is not about what you believe; it's not about a speech you make. It's about working hard. I'm not just running on a promise for change. I'm running on 35 years of change. What we need is somebody who can deliver change. We don't need to be raising false hopes."[44] It came to be seen as the defining statement for her candidacy.

The morning before the primary, Clinton became "visibly emotional" in response to a friendly question from a voter.[45] Video of the moment was replayed on cable news television throughout the day, accompanied by pundit commentary that ranged from sympathetic to callous in tone. Voters rallied to Clinton's defense, and she won a surprising 3% victory over Obama in the popular vote. They tied in the delegate count. Richardson withdrew from the race on January 10. Momentum shifted in Clinton's favor, and she won the popular vote in the Nevada caucuses eleven days later, despite Obama's endorsement from the influential Culinary Workers Union. However, Obama ran strongly in rural areas throughout the state, and he beat Clinton in the delegate count. Edwards' support collapsed in Nevada, as voters coalesced around the two apparent frontrunners. Dennis Kucinich withdrew from the race. In the following week, issues regarding race came to the fore as campaigning began for the South Carolina primary, the first to feature a large proportion of African Americans in the Democratic electorate. Behind in the state polls, Clinton left to campaign in some Super Tuesday states,[46] while her husband, former president Bill Clinton, stayed in South Carolina and engaged in a series of exchanges with Obama.[47] CBS News reported, "By injecting himself into the Democratic primary campaign with a series of inflammatory and negative statements, Bill Clinton may have helped his wife's presidential hopes in the long term but at the cost of his reputation with a group of voters [African Americans] that have long been one of his strongest bases of political support."[48]

Obama won by a more than two-to-one margin over Clinton, gaining 55% of the vote to her 27% and Edwards's 18%.[49] On the day of the primary, Bill Clinton compared Obama's expected win to Jesse Jackson's victory in the 1988 South Carolina Democratic primary. His comments were widely criticized as an apparent attempt to dismiss the primary results and marginalize Obama by implying that he was "the black candidate."[50] The momentum generated by Obama's larger-than-expected win in South Carolina was deflated somewhat by the win Clinton claimed in the nullified Florida primary the following week. Edwards suspended his candidacy on January 30. He did not immediately endorse either Clinton or Obama, but he said they both had pledged to carry forward his central campaign theme of ending poverty in America. Neither Clinton nor Obama had a clear advantage heading into the February 5 Super Tuesday primaries, with 23 states and territories and 1,681 delegates at stake and more media attention than any primary election day in American history.

Disputed primaries
In August 2006, the Democratic National Committee adopted a proposal by its Rules and Bylaws Committee stating that only the four states of Iowa, New Hampshire, Nevada, and South Carolina would be permitted to hold primaries or caucuses before February 5, 2008.[51] In May 2007, the Florida Legislature passed a bill that moved the date of the state's primary to January 29, 2008, setting up a confrontation with the DNC.[52] In response, the DNC ruled that Florida's 185 pledged delegates and 26 superdelegates would not be seated at the Democratic National Convention, or, if seated, would not be able to vote.[53] In October 2007, Democrats from Florida's congressional delegation filed a federal lawsuit against the DNC to force a recognition of its delegates, but the suit was unsuccessful.[51][54] The presidential candidates promised not to campaign in Florida.

Meanwhile, Michigan moved its primary to January 15, 2008, also in violation of party rules. In October 2007, Obama, Richardson, Biden, and Edwards withdrew their names from the Michigan primary ballot, under pressure from the DNC and voters in Iowa and New Hampshire.[55] Kucinich unsuccessfully sought to remove his name from the ballot,[56] whereas Clinton and Dodd opted to remain on the ballot.[57] In December 2007, the DNC ruled that Michigan's 128 pledged delegates and 29 superdelegates would not count in the nominating contest unless it were held on a later date.[58] The Michigan Democratic party responded with a press release noting that the primary would proceed with Clinton, Dodd, Gravel, and Kucinich on the ballot. Supporters of Biden, Edwards, Richardson, and Obama were urged to vote "uncommitted" instead of writing in their candidates' names because write-in votes for those candidates would not be counted.[59]

None of the top candidates campaigned in Florida or Michigan. The events were described in the media as "beauty contests,"[60] and voter turnout in both states was relatively low when compared with record-high turnout in other states.[61] Nevertheless, Clinton claimed wins in Florida and Michigan, and she flew to Fort Lauderdale on the night of the Florida election to thank supporters for what she called a "tremendous victory."[62]

As the primaries continued, various groups tried to negotiate a resolution to the standoff between the DNC and the state parties. The Clinton campaign advocated first for the results to stand and then for a new round of voting to take place in Michigan and Florida, while the Obama campaign deferred the matter to the DNC, while expressing a wish that the delegations be seated in some form.[63] On all sides, Democrats worried that a failure to resolve the problem could lead to a rules or credential fight at the convention and low Democratic turnout in the general election in November.[60]

On May 31, 2008, the DNC Rules and Bylaws Committee[64][65] voted unanimously (27–0) to restore half-votes to all the Florida delegates, including superdelegates. The Michigan delegates were also given half-votes, with 69 delegates pledged to Hillary Clinton and 59 to Barack Obama; this proposed change passing by 19–8.[66][67]

| Details | Restored votes to the convention[66][67] | Pledged delegate vote count[31] | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Awarded by the DNC | Change notes |
Final estimate | |||||||||
| Date | Election link | Pledged | Super | Total | Obama | Clinton | Edwards | Obama | Clinton | Edwards | |
| January 15 | Michigan primary | 128 | 29[68] | 157 | 59 | 69 | 0 | 59 | 69 | 0 | |
| January 29 | Florida primary | 185 | 26[69] | 211 | 67 | 105 | 13 | [33] | 67 | 105 | 13 |
| – | Total | 313 | 55 | 368 | 126 | 174 | 13 | 126 | 174 | 13 | |
| – | To date | 448 | 93 | 543 | 189 | 222 | 39 | 214 | 220 | 16 | |
Super Tuesday

Traditionally, the Tuesday on which the greatest number of states hold primary elections is known as Super Tuesday. In 2007, many states moved their primaries or caucuses to early in the year so they could have greater influence over the race. As February 5 was the earliest date to be allowed by the Democratic National Committee, 23 states and territories moved their elections to that date. 2008's Super Tuesday became the date of the nation's first quasi-national primary. It was dubbed "Super Duper Tuesday"[70] or "Tsunami Tuesday,"[71] among other names.

After Obama's win in the South Carolina primaries on January 26, he received high-profile endorsements from Caroline Kennedy, daughter of former President John F. Kennedy,[72] as well as Senator Ted Kennedy, the former President's brother.[73] Ted Kennedy's endorsement was considered "the biggest Democratic endorsement [that] Obama could possibly get short of Bill Clinton or Al Gore."[74] On January 31, Obama and Clinton met for the first time in a one-on-one debate, and they struck a friendly tone.[75][failed verification] Obama surged nationally in the polls and held campaign rallies that drew audiences of over 15,000 people in several states.[76]

A total of 1,681 pledged delegate votes were at stake in the states that voted on February 5. The following table shows the pledged delegate votes awarded in the Super Tuesday states.

| Details | Delegate votes to the convention | Pledged delegate vote count[31] | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Election result | Change notes |
Final estimate | ||||||
| Election link | Pledged | Super | Total | Obama | Clinton | Obama | Clinton | |
| Alabama primary | 52 | 8 | 60 | 27 | 25 | 27 | 25 | |
| Alaska caucuses | 13 | 4 | 17 | 9 | 4 | [77] | 10 | 3 |
| American Samoa caucuses | 3 | 6 | 9 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | |
| Arizona primary | 56 | 11 | 67 | 25 | 31 | 25 | 31 | |
| Arkansas primary | 35 | 12 | 47 | 8 | 27 | 8 | 27 | |
| California primary | 370 | 71 | 441 | 166 | 204 | 166 | 204 | |
| Colorado caucuses | 55 | 15 | 70 | 35 | 20 | [78] | 36 | 19 |
| Connecticut primary | 48 | 12 | 60 | 26 | 22 | 26 | 22 | |
| Delaware primary | 15 | 8 | 23 | 9 | 6 | 9 | 6 | |
| Georgia primary | 87 | 15 | 102 | 60 | 27 | 60 | 27 | |
| Idaho caucuses | 18 | 5 | 23 | 15 | 3 | 15 | 3 | |
| Illinois primary | 153 | 31 | 184 | 104 | 49 | 104 | 49 | |
| Kansas caucuses | 32 | 9 | 41 | 23 | 9 | 23 | 9 | |
| Massachusetts primary | 93 | 28 | 121 | 38 | 55 | 38 | 55 | |
| Minnesota caucuses | 72 | 16 | 88 | 48 | 24 | 48 | 24 | |
| Missouri primary | 72 | 16 | 88 | 36 | 36 | 36 | 36 | |
| New Jersey primary | 107 | 20 | 127 | 48 | 59 | 48 | 59 | |
| New Mexico primary | 26 | 12 | 38 | 12 | 14 | 12 | 14 | |
| New York primary | 232 | 49 | 281 | 93 | 139 | 93 | 139 | |
| North Dakota caucuses | 13 | 8 | 21 | 8 | 5 | 8 | 5 | |
| Oklahoma primary | 38 | 10 | 48 | 14 | 24 | 14 | 24 | |
| Tennessee primary | 68 | 17 | 85 | 28 | 40 | 28 | 40 | |
| Utah primary | 23 | 6 | 29 | 14 | 9 | 14 | 9 | |
| Total | 1,681 | 390 | 2,071 | 847 | 834 | 849 | 832 | |
| To date | 2,129 | 483 | 2,614 | 1,036 | 1,056 | 1,063 | 1,052 | |
On election night, both Obama and Clinton claimed victories. In the popular vote, Obama won 13 states and territories to Clinton's 10. This included the states of Idaho and Georgia, where Obama won by very wide margins. His wins in Connecticut and Missouri were considered upsets. However, Clinton won the large electoral prizes of California and Massachusetts, where some analysts had expected the Kennedy endorsements might carry Obama to the victory. Although Obama gained significant ground from where he was polling in mid-January, it was not enough to close the gap in those states. In exit polls, Obama gained some overwhelming support of African-American voters, and he strengthened his base among college-educated voters and voters younger than the age of 45. Clinton found significant support among white women, Latinos, and voters over age 65. Obama ran strongest in caucus states, Rocky Mountain states, Southern states and Midwestern states. Clinton ran strongest in the Northeastern states, Southwestern states, and states bordering Arkansas, where she served as first lady while her husband served as that state's governor. When the delegate counting was finished, Obama won an estimated 847 pledged delegates to Clinton's 834. Early in the primary season, many observers had predicted that the nomination would be over after Super Tuesday, but the general verdict on election night was that the candidates had drawn to a virtual tie and that the race for the Democratic presidential nomination would not likely be settled for at least a month.[79]

Mid-February contests
In the following week, it became clear that a tie on Super Tuesday would leave Obama better positioned for the upcoming contests in February, where the demographics of several large states seemed to favor him.[80] The day after Super Tuesday, February 6, Clinton announced that she had personally lent her campaign $5 million in January.[79] The news came as a surprise and set off another round of news stories about Clinton donors and supporters concerned about the campaign's strategy. It was particularly striking in light of Obama's announcement that he had raised a record-high $32 million in January, tapping 170,000 new contributors.[81] It became clear that Obama's financial advantage had allowed him to organize and compete in some broader states on Super Tuesday, an advantage that was likely to continue in the upcoming months and weeks. In response, Clinton's supporters raised $6 million online in 36 hours, but Obama's campaign upped the ante, announcing their own total of $7.5 million in 36 hours and starting a new goal of reaching 500,000 new contributors in 2008 by late February.[82]

| Details | Delegate votes to the convention | Pledged delegate vote count[31] | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Election result | Change notes |
Final estimate | |||||||
| Date | Election link | Pledged | Super | Total | Obama | Clinton | Obama | Clinton | |
| February 9 | Louisiana primary | 56 | 11 | 67 | 33 | 23 | 33 | 23 | |
| Nebraska caucuses | 24 | 7 | 31 | 16 | 8 | 16 | 8 | ||
| U.S. Virgin Islands convention | 3 | 6 | 9 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 0 | ||
| Washington caucuses[83][84] | 78 | 19 | 97 | 52 | 26 | 52 | 26 | ||
| February 10 | Maine caucuses | 24 | 8 | 32 | 15 | 9 | 15 | 9 | |
| February 5–12 | Democrats Abroad primary | 7 | 4 | 11 | 4½ | 2½ | 4½ | 2½ | |
| February 12 | D.C. primary | 15 | 24 | 39 | 12 | 3 | [85] | 13 | 2 |
| Maryland primary | 70 | 28[86] | 98 | 42 | 28 | [87] | 43 | 27 | |
| Virginia primary | 83 | 18 | 101 | 54 | 29 | 54 | 29 | ||
| February 19 | Hawaii caucuses | 20 | 9 | 29 | 14 | 6 | 14 | 6 | |
| Wisconsin primary | 74 | 18 | 92 | 42 | 32 | 42 | 32 | ||
| – | Total | 454 | 152 | 606 | 287½ | 166½ | 289½ | 164½ | |
| – | To date | 2,583 | 635 | 3,220 | 1,323½ | 1,222½ | 1,352½ | 1,216½ | |

As expected, Obama swept the three nominating events on February 9, which were thought to favor him based on the results in similar states that had voted previously. He then scored a convincing win in Maine, where Clinton had hoped to hold her ground.[88] The same day, Clinton's campaign announced that campaign advisor Patti Solis Doyle would resign. Obama's momentum carried throughout the following week, as he scored large delegate gains in the Potomac primaries, taking the lead in the nationwide popular vote, even under the projection most favorable to Clinton, with Florida and Michigan included. NBC News declared him "Mr. Frontrunner" on February 13.[89] Clinton attempted a comeback win in the demographically more favorable state of Wisconsin, but Obama won again by a larger margin than expected. In 11 days, he swept 11 contests and extended his pledged delegate lead by 120. By the end of the month, Obama had 1,192 pledged delegates to Clinton's 1,035. He also began closing the gap in superdelegates, although Clinton still led among superdelegates by 240–191. Clinton's campaign tried to downplay the results of the February contests, and the candidate refused to acknowledge the losses in her speeches on election nights.[citation needed] Her advisers acknowledged that she would need big wins in the upcoming states to turn the race around.

March
With four states and 370 delegates at stake, March 4 was dubbed "Mini-Super Tuesday" or "Super Tuesday II". Just as Obama had been favored in the mid-February states, Clinton was favored in Ohio, with its high proportion of working-class white voters and older voters, and Texas, with its high proportion of Latino voters. Exit polls in previous states showed that all three groups were a part of Clinton's base. In mid-February, Clinton held a 10-point lead in Texas and a 20-point lead in Ohio in RealClearPolitics polling averages.[90] Her campaign set its sights on the Ohio-Texas "firewall," counting on a clear March 4 win to change the narrative and turn her campaign around for the nomination. Meanwhile, Obama hoped to win one or both states that might be enough to knock Clinton out of the race. By February 25, according to a CNN poll, they were in a statistical dead heat in Texas.[91]


In the last week of February, Clinton's campaign seemed to be back on its feet. A Saturday Night Live sketch mocked the media for its supposedly biased coverage in favor of Obama, and Clinton used the sketch to argue that Obama had not received proper scrutiny. The media responded by taking a more critical look at Obama's campaign.[92] Meanwhile, Obama supporter and former fundraiser Tony Rezko went on trial in a political corruption case in Chicago. While Obama was not implicated, questions remained about how forthcoming he had been about his relationship with Rezko.[92] Controversy also erupted when it was reported in the Canadian press that Obama economic advisor Austan Goolsbee had privately offered assurances that Obama's anti-North American Free Trade Agreement rhetoric on the campaign trail was exaggerated. Obama's campaign denied the substance of the report, but their response was muddled by a series of missteps and may have hurt the candidate's standing with Ohio voters.[93] Clinton launched a five-point attack on Obama's qualifications, "unleashing what one Clinton aide called a 'kitchen sink' fusillade," according to The New York Times.[94] Perhaps the most damaging component was a campaign ad that aired in Texas, using the imagery of the White House "red phone" to suggest that Obama would not be prepared to handle a crisis as commander-in-chief when a phone call comes into the White House at 3 a.m. The ad drew significant media attention in the four days before the election.[95] In the general-election campaign, McCain used parts of the ad against Obama.[96]

| Details | Delegate votes to the convention | Pledged delegate vote count[31] | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Election result | Change notes |
Final estimate | |||||||
| Date | Election link | Pledged | Super | Total | Obama | Clinton | Obama | Clinton | |
| March 4 | Ohio primary | 141 | 21 | 162 | 67 | 74 | 67 | 74 | |
| Rhode Island primary | 21 | 12 | 33 | 8 | 13 | 8 | 13 | ||
| Texas primary[97] | 126 | 35 | 228 | 61 | 65 | 61 | 65 | ||
| Texas caucuses[97] | 67 | 38 | 29 | [98] | 38 | 29 | |||
| Vermont primary | 15 | 8 | 23 | 9 | 6 | 9 | 6 | ||
| March 8 | Wyoming caucuses | 12 | 6 | 18 | 7 | 5 | 7 | 5 | |
| March 11 | Mississippi primary | 33 | 8 | 41 | 20 | 13 | 20 | 13 | |
| – | Total | 415 | 90 | 505 | 210 | 205 | 210 | 205 | |
| – | To date | 2,998 | 725 | 3,725 | 1,533½ | 1,427½ | 1,562½ | 1,421½ | |
On election night, Clinton scored convincing wins in Ohio and Rhode Island. She narrowly won the Texas primary, while losing the Texas caucus. She pitched her wins that night as a comeback: "For everyone here in Ohio and across America who's ever been counted out but refused to be knocked out, and for everyone who has stumbled but stood right back up, and for everyone who works hard and never gives up, this one is for you."[99]

Obama focused on the "delegate math." He won the total delegate count in Texas, and he stayed close to Clinton on the delegate count in Ohio. "No matter what happens tonight," he said, "we have nearly the same delegate lead that we did this morning, and we are on our way to winning this nomination."[100] In fact, March 4 was the first election day in which Clinton won more delegates than Obama (though the Florida and Michigan primaries would later be honored by seating half of the states' delegations). After winning contests in Wyoming and Mississippi the following week, Obama erased Clinton's March 4 gains. On March 15, he increased his lead by 10 delegates at the Iowa county conventions, when former supporters of withdrawn candidates switched their support to him.

After the March contests, the Democratic race entered a six-week period with no upcoming contests until April 22. As the campaigns settled in for the long haul, advisors for both candidates escalated their rhetoric and stepped up attacks in their daily conference calls. News reports described the tenor as increasingly "rancorous" and "vitriolic."[101]

On March 14, clips of controversial sermons from Obama's former pastor, Jeremiah Wright, resurfaced on YouTube and received heavy airtime on cable news television. Among other things, Wright said, "God damn America for treating our citizens as less than human. God damn America for as long as she acts like she is God and she is supreme." Four days later, Obama responded to the controversy in a 37-minute speech, speaking openly about race and religion in the United States. He denounced Wright's remarks while refusing to condemn the pastor himself, and he attempted to pivot from the immediate circumstances to address the larger theme of "A More Perfect Union." The speech was regarded as "breathtakingly unconventional" in its political strategy and tone,[102] and it received generally positive reviews in the press. The New York Times weighed in with an editorial: "Senator Barack Obama, who has not faced such tests of character this year, faced one on Tuesday. It is hard to imagine how he could have handled it better."[103] Ten days later, the speech had been watched at least 3.4 million times on YouTube.[104]

On March 21, former primary candidate Bill Richardson, who has previously held important posts in the Clinton Administration, endorsed Barack Obama, a move that drew intense criticism from Clinton allies, including James Carville's Eastertime comparison of Richardson with Judas Iscariot.[105] On March 25, Mike Gravel announced that he would leave the Democrats and join the Libertarian Party, entering the race for the 2008 Libertarian presidential nomination the following day.[106]

April and beyond

As the race continued to Pennsylvania, Indiana, and North Carolina, many observers concluded that Clinton had little chance to overcome Obama's lead in pledged delegates.[108] Even if she were to succeed in changing the dynamics of the race, there would not be enough pledged delegates remaining for her to catch up under most realistic scenarios.[109] Some analysts believed Clinton could still win the nomination by raising doubts about Obama's electability, fighting for Michigan and Florida delegates to be seated at the convention, and convincing superdelegates to support her despite her expected loss in the pledged delegate vote.[110] However, the window of opportunity for re-votes in Michigan and Florida appeared to close in late March,[109] and House Speaker Nancy Pelosi, chairwoman of the Democratic National Convention, said that it would be harmful to the party if superdelegates were to overturn the result of the pledged delegate vote.[111]

Complicating the equation for Democrats, presidential candidate John McCain clinched the Republican nomination on March 4. With Obama and Clinton engaged in the Democratic primary, McCain was free to define his candidacy for the general election largely unchallenged. Some Democrats expressed concern that Clinton stayed in the campaign through March and April, when they felt she had little chance to win the nomination, but a much greater chance to damage Obama's candidacy in the general election. However, others defended Clinton's right to continue on, arguing that a sustained campaign was good for the Democratic Party and that Clinton still had a realistic shot at the nomination.[112]

On April 22, Clinton scored a convincing win in Pennsylvania. However, on May 6, Obama surprised many observers by winning North Carolina by almost 15 percentage points, effectively erasing Clinton's gains in Pennsylvania. Clinton won by only 1 point in Indiana. With Obama now leading by 164 pledged delegates and with only 217 pledged delegates left to be decided in the remaining contests, many pundits declared that the primary was effectively over. Obama gave an election night speech that looked forward to the general election campaign against McCain.[113] The pace of superdelegate endorsements increased. On May 10, Obama's superdelegate total surpassed Clinton's for the first time in the race, making the math increasingly difficult for a Clinton win.[114]

Clinton vowed to continue campaigning, and won convincingly in primaries in West Virginia on May 13, and Kentucky on May 20 where Appalachian voters strongly preferred her over Obama. However, Obama was able to clear a victory in Oregon on May 20, which allowed him to clinch the majority of pledged delegates. Obama gave a speech in Des Moines, Iowa, the state that propelled his candidacy, in which he stated, "You have put us within reach of the Democratic nomination for president of the United States of America."[115] Clinton advisers said they would appeal to the DNC's Rules & Bylaws Committee[116][117] to have the Michigan and Florida delegations seated. However, even under the most favorable seating arrangement, she would not have been able to take a lead in pledged delegates and would have had to rely on superdelegates to win the nomination. On May 31, the rules committee accepted the Michigan state party's 69-59 distribution of pledged delegates and restored half votes to Florida's and Michigan's delegations. This resulted in a net gain for Clinton of 24 pledged delegates. Obama remained significantly ahead, with a lead of 137 pledged delegates before the Puerto Rico primary on June 1.

On June 3, the day of the final primaries in South Dakota and Montana, Obama rolled out about sixty superdelegate endorsements. Those endorsements, together with the pledged delegates awarded in the final primaries, put him well over the "magic number" of 2,117 delegate votes necessary for a majority at the Democratic National Convention. By early in the evening, all major news organizations had announced that Obama had clinched the Democratic nomination, and Obama claimed the status of presumptive nominee in a speech in St. Paul, Minnesota. Clinton did not concede the nomination in her election night speech, saying that she would be "making no decisions tonight".[118] On the morning of June 5, Clinton posted on her website an open letter to her supporters, which she also sent by e-mail that day. It announced that on Saturday (June 7) Clinton would endorse Obama's candidacy. During a well received concession speech in Washington DC on Saturday June 7 Clinton endorsed Obama in the following terms: "The way to continue our fight now, to accomplish the goals for which we stand is to take our energy, our passion, our strength, and do all we can to help elect Barack Obama, the next president of the United States. Today, as I suspend my campaign, I congratulate him on the victory he has won and the extraordinary race he has run. I endorse him and throw my full support behind him."

| Details | Delegate votes to the convention | Pledged delegate vote count[31] | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Election result | Change notes |
Final estimate | ||||||||
| Date | Election link | Pledged | Super | Total | Obama | Clinton | Obama | Clinton | ||
| April 22 | Pennsylvania primary | 158 | 29 | 187 | 73 | 85 | 73 | 85 | ||
| May 3 | Guam caucuses | 4 | 5 | 9 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | ||
| May 6 | Indiana primary | 72 | 13 | 85 | 34 | 38 | 34 | 38 | ||
| North Carolina primary | 115 | 19 | 134 | 67 | 48 | 67 | 48 | |||
| May 13 | West Virginia primary | 28 | 11 | 39 | 8 | 20 | 8 | 20 | ||
| May 20 | Kentucky primary | 51 | 9 | 60 | 14 | 37 | 14 | 37 | ||
| Oregon primary | 52 | 13 | 65 | 31 | 21 | 31 | 21 | |||
| June 1 | Puerto Rico primary | 55 | 8 | 63 | 17 | 38 | 17 | 38 | ||
| June 3 | Montana primary | 16 | 9 | 25 | 9 | 7 | 9 | 7 | ||
| South Dakota primary | 15 | 8 | 23 | 6 | 9 | 6 | 9 | |||
| – | At-large vacancies* | – | 2 | 2 | ||||||
| – | Total | 566 | 126 | 692 | 261 | 305 | 261 | 305 | ||
| – | To date | 3,564 | 851 | 4,417 | 1,794½ | 1,732½ | 1,823½ | 1,726½ | ||
* Two at-large DNC superdelegate seats are vacant, see: History of superdelegate composition changes.

Results
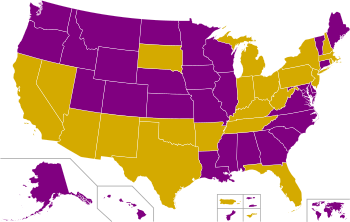
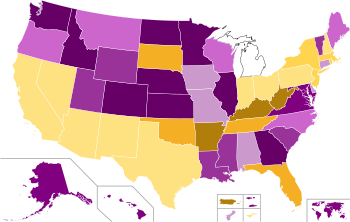
Below are the results for the state primaries and caucuses held by the Democratic Party in 2008 for the presidential primaries.[1] [2] Clinton won one territorial contest, Puerto Rico, whilst Obama won Guam, the US Virgin Islands and American Samoa. He also won the District of Columbia.


- 20–30%
- 30–40%
- 40–50%
- 50–60%
- 60–70%
- 70–80%
- 80–90%
- 90–100%
- 100%
- 30–40%
- 40–50%
- 50–60%
- 60–70%
- 70–80%
- 80–90%
- 90–100%
- 100%
- 20–30%
- 30–40%
- 40–50%
- 40–50%

N.B: The grey counties in Michigan denote that the counties are uncommitted for either candidate.

Voter turnout

Voter turnout was at historically high levels in the 2008 primaries and caucuses, with many contests setting all-time records for turnout. Voter turnout on Super Tuesday was at 27% of eligible citizens, breaking the previous record of 25.9% set in 1972.[119] Turnout was higher among Democrats than Republicans, with Democratic turnout surpassing Republican turnout even in traditionally red states where the number of registered Democrats is proportionally low.[120] Many states reported high levels of Democratic voter registration in the weeks before primaries.[121] From January 3 through February 5, Democratic turnout exceeded Republican turnout, 19.1 million to 13.1 million.[122]

In the first five weeks of 2008, 'voter turnout' was a phrase that was used almost exclusively in connection with the Democratic Party. There were routine stories of precincts running short on ballots, poll hours being extended, and voters packing haunch to paunch inside community centers and local churches. Crowd sizes were described, often with growing awe, as 'staggering,' 'record breaking,' or 'unprecedented.'
— Kent Garber, U.S. News & World Report[122]
The high Democratic turnout was attributed to several factors:[123]

- the compressed primary calendar, which gave voters in more states an opportunity to participate in the nomination
- media interest and voter excitement generated by the first viable African-American and female presidential contenders
- dissatisfaction with Republican presidential candidates
- the early emergence of John McCain as the presumptive nominee of the Republican Party
- open primaries in some states, which allowed Republicans and independent voters to participate in Democratic contests
- dissatisfaction with President George W. Bush and Iraq War policy
- cyclical party realignment
See also
- Fundraising for the 2008 United States presidential election
- Nationwide opinion polling for the 2008 Democratic Party presidential primaries
- Political positions of Barack Obama
- Political positions of Hillary Clinton
- 2008 Republican Party presidential primaries
- Statewide opinion polling for the 2008 Democratic Party presidential primaries
- 2016 Democratic Party presidential primaries
Notes
- ^ a b This figure does not include the states of Iowa, Nevada, Washington and Maine who did not release popular vote information. The political news and polling data aggregator website RealClearPolitics estimated that the results of the caucuses would have increased Obama's total vote to 17,869,542 and Clinton's to 17,717,698.[1] The Democratic National Committee (DNC) did not recognize primary results in Michigan, due to the state moving the date of their primary to January. Due to the lack of DNC recognition, Obama and several other candidates withdrew their names from the ballot whereas Clinton did not. The results of the Michigan primary were as thus: Uncommitted: 238,168; Clinton: 328,309. If the Michigan tally had been made official, the overall popular vote would be 17,535,458 for Obama and 17,822,145 for Clinton. With the caucuses estimates included the overall tally would be 17,869,542 and 18,046,007 respectively.[1][2]
References
- ^ a b c d e f "2008 Democratic Popular Vote". RealClearPolitics. Retrieved February 15, 2020.
- ^ a b Coomarasamy, Jamie (June 1, 2008). "Equal split masks Obama victory". BBC News. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ "Democratic Vote Count". Real Clear Politics. January 29, 2008. Retrieved March 7, 2012.
- ^ "Clinton and the Popular Vote". FactCheck.org. June 5, 2008. Retrieved May 13, 2016.
- ^ Weisman, Jonathan; et al. (June 4, 2008). "Strategy Was Based On Winning Delegates, Not Battlegrounds". The Washington Post. Retrieved June 4, 2008.
- ^ Pickler, Nedra (May 24, 2008). "AP: Obama's Political Team Out-Organized Clinton". The Huffington Post. Huffingtonpost.com. Retrieved March 7, 2012.
- ^ a b c "2008 Democratic Convention Watch". June 6, 2008. Retrieved June 7, 2008.
- ^ a b The pledged delegate estimates come from the sum of the states listed in the Chronicle section in this article.
- ^ "Clinton to suspend campaign Saturday". NBC News. June 4, 2008. Retrieved June 4, 2008.
- ^ "Clinton to suspend her campaign on Saturday". CNN. May 14, 2008. Retrieved May 14, 2008.
- ^ "Democratic Delegate Allocation – 2008". Retrieved March 14, 2008.
- ^ "Why delegates matter in the presidential race". CNN. January 3, 2008. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ a b c "Delegate Selection Rules for the 2008 Democratic National Convention" (PDF). Democratic National Committee. August 19, 2006. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 6, 2010. Retrieved January 21, 2008.
- ^ "FAQ's". Nevada State Democratic Party. Archived from the original on January 23, 2008. See also: "Iowa Democratic Party Precinct Caucus Fact Sheet". Iowa Democratic Party. Archived from the original on July 3, 2007.
- ^ Tibbetts, Ed (December 15, 2007). "So why DO we caucus, anyway?". Quad-City Times.
- ^ "Call for the 2008 Democratic National Convention" (PDF). Democratic National Committee. March 17, 2008. p. 33. Archived from the original (PDF) on June 8, 2011. Retrieved March 17, 2008.
- ^ "Campaign Finance: First Quarter 2007 FEC Filings", The Washington Post, 2007.
- ^ Balz, Dan (April 27, 2007). "Candidates Unite in Criticizing Bush". The Washington Post. Retrieved May 30, 2007.
- ^ Seelye, Katharine (November 21, 2007). "Oprah May Campaign for Obama". The New York Times. Retrieved March 21, 2008.
- ^ "Oprah to aid Obama in D.M., Cedar Rapids". Des Moines Register.[permanent dead link]
- ^ "Hillary Loses Iowa Lead". Arabnews.com. December 4, 2007. Retrieved March 7, 2012.
- ^ Zeleny, Jeff (December 8, 2007). "Oprah in Des Moines". The New York Times. Retrieved March 23, 2008.
- ^ Pindell, James (December 9, 2007). "Oprah-Obama double bill largest political NH rally in recent memory". The Boston Globe. Retrieved March 23, 2008.
- ^ Fineman, Howard (December 8, 2007). "Fineman: Obama's Oprah Challenge – The Daily Beast". Newsweek.com. Retrieved March 7, 2012.
- ^ Murray, Mark (December 10, 2007). "First Thoughts: All tied up". MSNBC. Archived from the original on March 28, 2008. Retrieved March 23, 2008.
- ^ "The Oprah Winfrey Show (and Obama was there too)". The Independent. London. December 10, 2007. Archived from the original on January 2, 2008. Retrieved March 23, 2008.
- ^ "Sweet: New poll puts Obama in solid Iowa lead for first time. Crucial momenteum before Thursday caucus". Chicago Sun-Times. Archived from the original on March 27, 2008. Retrieved February 21, 2009.
- ^ "Rasmussen Reports: Daily Presidential Tracking Polling History". Archived from the original on March 5, 2008.
- ^ "RealClear Politics, Final Polls, Iowa Democratic Caucus".
- ^ "Highlights of the 2008 Rules". The Democratic Party. Archived from the original on August 22, 2006.
- ^ a b c d e f Sources are indicated at each state's primary or caucus article, reached by following the appropriate "Election link."
- ^ Several candidates have withdrawn their nomination bids since the Iowa caucuses on January 3. At the Iowa county conventions on March 15 and the district conventions on April 26, some delegates supporting the withdrawn candidates moved their support to Obama.
- ^ a b "2008 Democratic Convention Watch: What happens to Edwards' delegates?". Democratic Convention Watch. June 4, 2008. Retrieved June 4, 2008.
Edwards still has 3 state-wide delegates from Iowa, which will be allocated at the Iowa State Convention on June 14. They will remain in Edwards column until then.
- ^ After John Edwards withdrew from the race and subsequently endorsed Barack Obama on May 14, a delegate supporting Edwards announced an intention to support Obama at the national convention.
- ^ Higher turnout from Obama supporters at the Nevada state convention on May 17 resulted in a 14–11 delegate split, in contrast to the 13-12 split predicted by the precinct caucuses on January 19. See: Obama flips Clinton's Nevada win; captures more national delegates [dead link], Inside Nevada Politics, May 17, 2008.
- ^ After John Edwards withdrew from the race and subsequently endorsed Barack Obama on May 14, some delegates supporting Edwards announced their intention to support Obama at the national convention.
- ^ Rhee, Foon (January 3, 2008). "Obama says time for change has come". The Boston Globe. Retrieved January 4, 2008.
- ^ a b Nichols, Bill (January 3, 2008). "Obama and Huckabee win big in Iowa". politico.com. Retrieved January 3, 2008.
- ^ Tumulty, Karen (January 5, 2008). "Clinton Machine Shaken By Setback". Time. Archived from the original on January 6, 2008. Retrieved January 5, 2008. See also: Kornblut, Anne E.; Jonathan Weisman; Paul Kane (January 5, 2008). "Clinton's Supporters Question Her Strategy". The Washington Post. Retrieved January 5, 2008.
- ^ Kornblut, Anne E. (January 8, 2008). "A Clinton Campaign Shakeup?". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on May 23, 2011. Retrieved January 9, 2008.
- ^ Dionne, E. J. (January 8, 2008). "A Candidacy's Prose and Cons". The Washington Post. Retrieved January 9, 2008.
- ^ "RealClearPolitics New Hampshire Polling Average".
- ^ Healy, Patrick; Jeff Zelaney (January 6, 2008). "At Debate, Two Rivals Go After Defiant Clinton". The New York Times. Retrieved January 7, 2008.
- ^ Memmott, Mark; Jill Lawrence (January 6, 2008). "Edwards: He & Obama share a 'conviction alliance'". USA Today. Archived from the original on January 17, 2008. Retrieved January 6, 2008.
- ^ "Clinton chokes up, is applauded, at campaign stop". CNN. January 7, 2008. Retrieved January 7, 2008.
- ^ "Hillary Clinton Bill Clinton South Carolina". Huffington Post.
- ^ [citation needed]
- ^ Ververs, Vaughn (January 26, 2008). "Analysis: Bill Clinton's Lost Legacy". CBS News. San Francisco, CA: CBS Interactive Inc. Archived from the original on June 5, 2014. Retrieved April 19, 2015.
- ^ "Obama claims big win in South Carolina". CNN. January 26, 2008. Retrieved January 26, 2008.
- ^ "Bubba: Obama is like Jesse Jackson". ABCNews.com. January 26, 2008. Retrieved March 10, 2008.
- ^ a b Tomasky, Michael (March 20, 2008). "A Possibly Super Problem". New York Review of Books. Retrieved March 15, 2008.
- ^ "This bill does a lot more than advertised". May 8, 2007. Retrieved March 11, 2008.
- ^ "Orlando Sentinel Blogs". Orlando Sentinel. July 21, 2007. Archived from the original on October 29, 2007. Retrieved July 24, 2007.
- ^ "Can the Democratic Party Ignore Florida's Primary". The Christian Science Monitor. October 16, 2007. Retrieved March 20, 2008.
- ^ "Four Candidates Withdraw from Michigan Primary Ballot" (Press release). Michigan Department of State. October 9, 2007. Archived from the original on January 16, 2008. Retrieved January 10, 2008.
- ^ Gorchow, Zachary (January 3, 2008). "Kucinich says he'll come to Michigan after all". Detroit Free Press. Archived from the original on November 9, 2013. Retrieved January 14, 2008.
- ^ Hoffman, Kathy Barks (October 10, 2007). "Clinton In, 5 Dems Out of Mich. Primary". Guardian Unlimited. London. Associated Press. Retrieved January 14, 2008. [dead link]
- ^ Ohlemacher, Stephen (December 2, 2007). "Democrats Strip Michigan of Delegates". WKRN. Associated Press. Archived from the original on December 3, 2007. Retrieved January 14, 2008.
- ^ "MDP Releases Voter Guide To Help Voters Understand Presidential Primary" (Press release). Michigan Democratic Party. December 10, 2007. Archived from the original on January 15, 2008. Retrieved January 10, 2008.
- ^ a b Balz, Dan (February 9, 2008). "Sanctioned States Put Democrats in Quandary". The Washington Post. Retrieved March 20, 2008. See also: Sheinin, Aaron Gould (March 6, 2008). "Thurmond backs re-voting in Florida, Michigan". The Atlanta Journal-Constitution. Retrieved March 20, 2008.
- ^ Krunholz, June (March 19, 2008). "Disenfranchising Non-Voters in Florida and Michigan?". The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved March 20, 2008.
- ^ Broder, John M. (January 30, 2008). "Clinton Wins in Florida, but Without Any Delegates to Sweeten the Victory". The New York Times. Retrieved March 20, 2008.
- ^ Luo, Michael; John M. Broder (February 15, 2008). "Delegate Battles Snarl Democrats in Two States". The New York Times. Retrieved March 20, 2008. See also: Mooney, Alexander (March 20, 2008). "Obama: Wright flap has 'shaken me up'". CNN. Retrieved March 20, 2008.
- ^ "Rules and Bylaws Committee membership". 2008 Democratic Convention Watch. April 28, 2008. Retrieved May 31, 2008.
- ^ "Regulations of the Rules & Bylaws Committee For the 2008 Democratic National Convention (amended)" (PDF). DNC. February 1, 2007. Archived from the original (PDF) on May 28, 2008. Retrieved May 31, 2008.
- ^ a b Parnes, Amie; Avi Zenilman (May 31, 2008). "DNC panel agrees to seat Mich., Fla". Politico. Retrieved June 4, 2008.
- ^ a b "Florida and Michigan Votes Seated". 2008 Democratic Convention Watch. May 31, 2008. Retrieved May 31, 2008.
- ^ +1 due to Brenda Lawrence becoming a DNC Member for National Conference of Democratic Mayors, filling a previous vacancy
- ^ Ken Curtis moved from Maine to Florida. (Florida +1; Maine -1)
- ^ Schneider, Bill (February 7, 2007). "It could all be over after 'Super Tuesday'". CNN. Retrieved June 3, 2007.
- ^ Todd, Chuck (May 10, 2007). "Will Tsunami Tuesday be an Afterthought?". NBC News.
- ^ Kennedy, Caroline (January 27, 2008). "A President Like My Father". The New York Times. Retrieved January 27, 2008.
- ^ Allen, Mike; Brown, Carrie Budoff (January 27, 2008). "Ted Kennedy embraces Obama". Politico. Retrieved January 27, 2008.
- ^ Zeleny, Jeff; Brian Knowlton (January 27, 2008). "Kennedy Plans to Back Obama Over Clinton". The New York Times. Retrieved January 27, 2008.
- ^ Balz, Dan; Anne E. Kornblut (February 1, 2008). "Head to Head, Clinton, Obama Shelve Rancor". The Washington Post. Retrieved March 20, 2008.
- ^ Rosenthal, Andrew (February 4, 2008). "Michelle, Maria, Caroline and Oprah on the Hustings in California". The New York Times. Retrieved March 20, 2008. See also: Collins, Gail (January 31, 2008). "Four's a Crowd". The New York Times. Retrieved March 20, 2008. See also: Zeleny, Jeff; Elisabeth Bumiller (February 3, 2008). "Candidates Scrambling As Wave of Votes Nears". The New York Times. Retrieved March 20, 2008.
- ^ The final result of the state convention on May 24 was a 10–3 split in pledged delegates. A 9–4 split had been predicted after the precinct caucuses on February 5. See 2008 Alaska Democratic presidential caucuses for details.
- ^ The final result of the state convention on May 17 and the district conventions was a 36–19 split. A 35–20 split had been predicted after the precinct caucuses on February 5. See 2008 Colorado Democratic presidential caucuses for details.
- ^ a b Hook, Janet; Mark Z. Barabak (February 6, 2008). "Obama, Clinton campaigns assess Super Tuesday results". Los Angeles Times. Archived from the original on February 9, 2008. Retrieved March 20, 2008.
- ^ Cillizza, Chris (February 7, 2008). "What's Next". The Fix. The Washington Post. Archived from the original on August 30, 2008. Retrieved March 20, 2008.
- ^ Zeleny, Jeff; Leslie Wayne (February 1, 2008). "Enlisting New Donors, Obama Reaped $32 Million in January". The New York Times. Retrieved March 20, 2008.
- ^ Healy, Patrick; Jeff Zeleny (February 8, 2008). "Obama Outshines Clinton at Raising Funds". The New York Times. Retrieved March 20, 2008.
- ^ Washington Democrats use the February 9 caucuses to award delegates and ignore the February 19 primary. See 2008 Washington Democratic presidential caucuses for details.
- ^ Yardley, William (February 18, 2008). "In Washington State Vote, Relevance Is an Issue". The New York Times.
- ^ Clinton pledged delegate Jack Evans has announced an intention to vote for Obama at the national convention. See Washington City Paper and Washington Post Archived October 7, 2008, at the Wayback Machine articles. See 2008 District of Columbia Democratic presidential primary for details.
- ^ Albert Wynn announced his resignation as U.S. Representative on March 28, 2008. (Maryland -1) See Helderman, Rosalind S.; Jeffrey H. Birnbaum (March 28, 2008). "Wynn Decides to Leave Congress Months Before His Term Expires". The Washington Post. Retrieved March 30, 2008.
- ^ In May, pledged Clinton delegate Jack B. Johnson said he would vote for Obama, and urge the entire Maryland delegation to do so also. See "Pr. George's Executive Switches To Obama", The Washington Post, May 13, 2008. See 2008 Maryland Democratic presidential primary for details.
- ^ Seelye, Katharine Q. (February 11, 2008). "Maine to Obama; Clinton Replaces Campaign Leader". The New York Times. Retrieved March 20, 2008.
- ^ Todd, Chuck; et al. (February 13, 2008). "First Thoughts: Mr. Front-Runner". First Read. NBC News. Archived from the original on April 1, 2008. Retrieved March 20, 2008.
- ^ RealClearPolitics, Texas Polling Average, RealClearPolitics, Ohio Polling Average
- ^ Steinhauser, Paul (February 25, 2008). "Poll: It's all tied up for Dems in Texas". CNN. Retrieved March 20, 2008.
- ^ a b Seelye, Katharine Q. (March 5, 2008). "News Coverage Changes, and So Does Tone of the Campaign". The New York Times. Retrieved March 20, 2008.
- ^ Brown, Carrie Budoff (March 4, 2008). "Conflicting Obama answers on NAFTA meeting". Politico. Retrieved March 20, 2008.
- ^ Healy, Patrick and Julie Bosman (February 26, 2008). "Clinton Campaign Starts 5-Point Attack on Obama". The New York Times. Retrieved March 20, 2008.
- ^ Seelye, Katharine Q.; Jeff Zeleny (March 22, 2008). "Clinton Questions Role of Obama in a Crisis". The New York Times. Retrieved March 24, 2008.
- ^ Glover, Mike (August 26, 2008). "McCain ad returns to Clinton's 3 a.m. phone call". USA Today. Retrieved December 28, 2016.
- ^ a b Under the rules of Texas's unique "two-step" system, 126 pledged delegates are chosen during the primary on March 4. The remaining 67 pledged delegates are chosen during a caucus process beginning March 4 and culminating in a state convention June 6–7.
- ^ The results from the Texas county conventions on March 29 predict a 37–30 split, in contrast to the precinct conventions on March 4, which predicted a 38–29 split. The June 6 convention changed the split to a 38–29 count for Obama. See 2008 Texas Democratic presidential primary and caucuses for details.
- ^ "Hillary Clinton's Ohio Primary Victory Speech".
- ^ Nagourney, Adam (March 5, 2008). "Big Wins for Clinton in Texas and Ohio; McCain Clinches Race as Foe Concedes". The New York Times. Retrieved March 20, 2008.
- ^ Seeyle, Katherine Q.; Julie Bosman (April 1, 2008). "Carrying Primary Scars Into the General Election". The New York Times. Retrieved April 1, 2008. See also: Cillizza, Chris (March 27, 2008). "FixCam: Obamacains and McClintons". The Fix. The Washington Post. Archived from the original on March 21, 2012. Retrieved April 1, 2008.
- ^ Carney, James (March 18, 2008). "Obama's Bold Gamble on Race". Time. Archived from the original on March 20, 2008. Retrieved April 1, 2008.
- ^ Opinion (March 19, 2008). "Mr. Obama's Profile in Courage". The New York Times. Retrieved March 19, 2008.
- ^ Stelter, Brian (March 27, 2008). "Finding Political News Online, the Young Pass It On". The New York Times. Retrieved March 27, 2008.
- ^ Nagourney, Adam; Jeff Zeleny (March 22, 2008). "First a Tense Talk With Clinton, Then Richardson Backs Obama". The New York Times. Retrieved March 24, 2008.
- ^ Elkins, Sarah (March 31, 2008). "Maverick Mike". Newsweek. Archived from the original on May 6, 2008. Retrieved April 1, 2008.
- ^ MARIA Gavrilovic, Maria (May 18, 2008), "Obama Takes His Message To Record Crowd", CBS News.
- ^ Alter, Jonathan. "Hillary's New Math Problem". Newsweek.
- ^ a b Nagourney, Adam (March 20, 2008). "Clinton Facing Narrower Path to Nomination". The New York Times. Retrieved March 20, 2008.
- ^ Cillizza, Chris (March 6, 2008). "Clinton's Blueprint for Victory". The Fix. The Washington Post. Archived from the original on July 25, 2008. Retrieved March 20, 2008.
- ^ "Pelosi's Delegate Stance Boosts Obama". ABC News. March 14, 2008. Retrieved April 1, 2008.
- ^ Nagourney, Adam; Carl Hulse (March 6, 2008). "Clinton Success Changes Dynamic In Delegate Hunt". The New York Times. Retrieved March 20, 2008.
- ^ Rutenberg, Jim (May 8, 2008). "Pundits Declare the Race Over". The New York Times. Retrieved May 8, 2008.
- ^ "Obama Takes Superdelegate Lead for the First Time". Fox News. May 10, 2008. Retrieved May 11, 2008.
- ^ "Obama's Remarks in Des Moines," transcript, NY Times, May 20, 2008. Accessed October 16, 2012.
- ^ "2008 Democratic Convention Watch: Rules and Bylaws Committee membership". 2008 Democratic Convention Watch. April 28, 2008. Retrieved May 9, 2008.
- ^ "Regulations of the Rules & Bylaws Committee For The 2008 Democratic National Convention" (PDF). Democratic Party of the United States. December 2, 2006. Archived from the original (PDF) on June 8, 2011. Retrieved May 9, 2008.
- ^ "Obama: I will be the Democratic nominee". CNN. June 3, 2008. Retrieved June 4, 2008.
- ^ Seelye, Katharine (February 7, 2008). "The Caucus: Records for Turnout". The New York Times. Retrieved March 9, 2008.
- ^ Herszenhorn, David (March 7, 2008). "Senate Democrats Hope for a Majority Not Seen in 30 Years: 60 Seats". The New York Times. Retrieved March 9, 2008.
- ^ Kaplan, Thomas (February 5, 2008). "Connecticut Sees Surge of Voters for Primary". The New York Times. Retrieved March 9, 2008.
- ^ a b Garber, Kent (March 7, 2008). "High Democratic Turnout Sends a Mixed Signal for November". U.S. News & World Report. Retrieved March 9, 2008.
- ^ Michael, Laris (February 12, 2008). "Tight Race and Deep Interest Augur Big Turnout Today". The Washington Post. Retrieved March 9, 2008. See also: Whoriskey, Peter (February 6, 2008). "GEORGIA: Low GOP Enthusiasm". The Washington Post. Retrieved March 9, 2008.
External links
![]() Media related to Democratic Party presidential primaries, 2008 at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Democratic Party presidential primaries, 2008 at Wikimedia Commons

See what we do next...
OR
By submitting your email or phone number, you're giving mschf permission to send you email and/or recurring marketing texts. Data rates may apply. Text stop to cancel, help for help.
Success: You're subscribed now !