
Superior colliculus
| Superior colliculus | |
|---|---|
 Diagram of the superior colliculus (L) of the human midbrain (shown in red) and surrounding regions. The superior colliculus is surrounded by a red ring and transparent red circle to indicate its location. | |
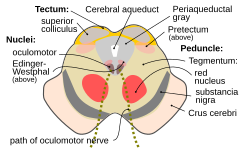 Section through midbrain at the level of the superior colliculus showing path of oculomotor nerve | |
| Details | |
| Part of | Tectum |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | colliculus superior |
| MeSH | D013477 |
| NeuroNames | 473 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_1040 |
| TA98 | A14.1.06.015 |
| TA2 | 5912 |
| TH | H3.11.03.3.01002 |
| TE | colliculus_by_E5.14.3.3.1.4.4 E5.14.3.3.1.4.4 |
| FMA | 62403 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
In neuroanatomy, the superior colliculus (from Latin 'upper hill') is a structure lying on the roof of the mammalian midbrain.[1] In non-mammalian vertebrates, the homologous structure is known as the optic tectum or optic lobe.[1][2][3] The adjective form tectal is commonly used for both structures.

In mammals, the superior colliculus forms a major component of the midbrain. It is a paired structure and together with the paired inferior colliculi forms the corpora quadrigemina. The superior colliculus is a layered structure, with a pattern that is similar in all mammals.[4] The layers can be grouped into the superficial layers (stratum opticum and above) and the deeper remaining layers. Neurons in the superficial layers receive direct input from the retina and respond almost exclusively to visual stimuli. Many neurons in the deeper layers also respond to other modalities, and some respond to stimuli in multiple modalities.[5] The deeper layers also contain a population of motor-related neurons, capable of activating eye movements as well as other responses.[6] In other vertebrates the number of layers in the homologous optic tectum varies.[4]

The general function of the tectal system is to direct behavioral responses toward specific points in body-centered space. Each layer contains a topographic map of the surrounding world in retinotopic coordinates, and activation of neurons at a particular point in the map evokes a response directed toward the corresponding point in space. In primates, the superior colliculus has been studied mainly with respect to its role in directing eye movements. Visual input from the retina, or "command" input from the cerebral cortex, creates a "bump" of activity in the tectal map which, if strong enough, induces a saccadic eye movement. Even in primates, however, the superior colliculus is also involved in generating spatially directed head turns, arm-reaching movements,[7] and shifts in attention that do not involve any overt movements.[8] In other species, the superior colliculus is involved in a wide range of responses, including whole-body turns in walking rats. In mammals, and especially primates, the massive expansion of the cerebral cortex reduces the superior colliculus to a much smaller fraction of the whole brain. It remains nonetheless important in terms of its function as the primary integrating center for eye movements.

In non-mammalian species the optic tectum is involved in many responses including swimming in fish, flying in birds, tongue-strikes toward prey in frogs, and fang-strikes in snakes. In some species, including fish and birds, the optic tectum, also known as the optic lobe, is one of the largest components of the brain.

Note on terminology: This article follows terminology established in the literature, using the term "superior colliculus" when discussing mammals and "optic tectum" when discussing either specific non-mammalian species or vertebrates in general.

Structure


The superior colliculus is a paired structure of the dorsal midbrain and is part of the midbrain tectum. The two superior colliculi are situated inferior/caudal to the pineal gland and the splenium of corpus callosum. They are overlapped by the pulvinar of the thalamus, and a medial geniculate nucleus of the thalamus is situated lateral to either superior colliculus.[9] The two inferior colliculi are situated immediately inferior/caudal to the superior colliculi; the inferior and superior colliculi are known collectively as the corpora quadrigemina (Latin for quadruplet bodies). The superior colliculi are larger than the inferior colliculi, though the inferior colliculi are more prominent.[10]

The brachium of superior colliculus (or superior brachium) is a branch that extends laterally from the superior colliculus, and, passing to the thalamus between the pulvinar and the medial geniculate nuclei, is partly continued into an eminence called the lateral geniculate nucleus, and partly into the optic tract.[citation needed]

The superior colliculus is associated with a nearby structure called the parabigeminal nucleus, often referred to as its satellite. In the optic tectum this nearby structure is known as the nucleus isthmi.[11]

The superior colliculus is a synaptic layered structure.[12] The microstructure of the superior colliculus and of the optic tectum, varies across species. As a general rule, there is always a clear distinction between superficial layers, which receive input primarily from the visual system and show primarily visual responses, and deeper layers, which receive many types of input and project to numerous motor-related brain areas. The distinction between these two zones is so clear and consistent that some anatomists have suggested that they should be considered separate brain structures.

In mammals, seven layers are identified[13] The top three layers are called superficial:

- Lamina I or SZ, the stratum zonale, is a thin layer consisting of small myelinated axons together with marginal and horizontal cells.
- Lamina II or SGS, the stratum griseum superficiale ("superficial gray layer"), contains many neurons of various shapes and sizes.
- Lamina III or SO, the stratum opticum ("optic layer"), consists mainly of axons coming from the optic tract.
Next come two intermediate layers:

- Lamina IV or SGI, the stratum griseum intermedium ("intermediate gray layer"), is the thickest layer, and is filled with many neurons of many sizes. This layer is often as thick as all the other layers together. It is often subdivided into "upper" and "lower" parts.
- Lamina V or SAI, the stratum album intermedium ("intermediate white layer"), consists mainly of fibers from various sources.
Finally come the two deep layers:

- Lamina VI or SGP, the stratum griseum profundum ("deep gray layer"), consists of loosely packed neurons and myelinated fibers.
- Lamina VII or SAP, the stratum album profundum ("deep white layer"), lying directly above the periaqueductal gray, consists entirely of fibers.
Neural circuitry
The superficial layers receive input mainly from the retina, vision-related areas of the cerebral cortex, and two tectal-related structures called the pretectum and parabigeminal nucleus. The retinal input encompasses the entire superficial zone, and is bilateral, although the contralateral portion is more extensive. The cortical input comes most heavily from the primary visual cortex (area 17, V1), the secondary visual cortex (areas 18 and 19), and the frontal eye fields. The parabigeminal nucleus plays a very important role in tectal function that is described below.

In contrast to the vision-dominated inputs to the superficial layers, the intermediate and deep layers receive inputs from a very diverse set of sensory and motor structures. Most areas of the cerebral cortex project to these layers, although the input from "association" areas tends to be heavier than the input from primary sensory or motor areas.[14] However, the cortical areas involved, and the strength of their relative projections, differ across species.[15] Another important input comes from the substantia nigra, pars reticulata, a component of the basal ganglia. This projection uses the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA, and is thought to exert a "gating" effect on the superior colliculus. The intermediate and deep layers also receive input from the spinal trigeminal nucleus, which conveys somatosensory information from the face, as well as the hypothalamus, zona incerta, thalamus, and inferior colliculus.

In addition to their distinctive inputs, the superficial and deep zones of the superior colliculus also have distinctive outputs. One of the most important outputs goes to the pulvinar and lateral intermediate areas of the thalamus, which in turn project to areas of the cerebral cortex that are involved in controlling eye movements. There are also projections from the superficial zone to the pretectal nuclei, lateral geniculate nucleus of the thalamus, and the parabigeminal nucleus. The projections from the deeper layers are more extensive. There are two large descending pathways, traveling to the brainstem and spinal cord, and numerous ascending projections to a variety of sensory and motor centers, including several that are involved in generating eye movements.

Both colliculi also have descending projections to the paramedian pontine reticular formation and spinal cord, and thus can be involved in responses to stimuli faster than cortical processing would allow.

Mosaic structure
On detailed examination, the collicular layers are actually not smooth sheets, but divided into a honeycomb arrangement of discrete columns.[16] The clearest indication of columnar structure comes from the cholinergic inputs arising from the parabigeminal nucleus, whose terminals form evenly spaced clusters that extend from top to bottom of the tectum.[17] Several other neurochemical markers including calretinin, parvalbumin, GAP-43, and NMDA receptors, and connections with numerous other brain structures in the brainstem and diencephalon, also show a corresponding inhomogeneity.[18] The total number of columns has been estimated at around 100.[16] The functional significance of this columnar architecture is not clear, but it is interesting that recent evidence has implicated the cholinergic inputs as part of a recurrent circuit producing winner-take-all dynamics within the tectum, as described in more detail below.

All species that have been examined — including mammals and non-mammals — show compartmentalization, but there are some systematic differences in the details of the arrangement.[17] In species with a streak-type retina (mainly species with laterally placed eyes, such as rabbits and deer), the compartments cover the full extent of the SC. In species with a centrally placed fovea, however, the compartmentalization breaks down in the front (rostral) part of the SC. This portion of the SC contains many "fixation" neurons that fire continually while the eyes remain fixed in a constant position.

Function
The history of investigation of the optic tectum has been marked by several large shifts in opinion. Before about 1970, most studies involved non-mammals — fish, frogs, birds — that is, species in which the optic tectum is the dominant structure that receives input from the eyes. The general view then was that the optic tectum, in these species, is the main visual center in the non-mammalian brain, and, as a consequence, is involved in a wide variety of behaviors.[19] From the 1970s to 1990s, however, neural recordings from mammals, mostly monkeys, focused primarily on the role of the superior colliculus in controlling eye movements. This line of investigation came to dominate the literature to such a degree that the majority opinion was that eye-movement control is the only important function in mammals, a view still reflected in many current textbooks.

In the late 1990s, however, experiments using animals whose heads were free to move showed clearly that the SC actually produces gaze shifts, usually composed of combined head and eye movements, rather than eye movements per se. This discovery reawakened interest in the full breadth of functions of the superior colliculus, and led to studies of multisensory integration in a variety of species and situations. Nevertheless, the role of the SC in controlling eye movements is understood in much greater depth than any other function.

Behavioral studies have shown that the SC is not needed for object recognition, but plays a critical role in the ability to direct behaviors toward specific objects, and can support this ability even in the absence of the cerebral cortex.[20] Thus, cats with major damage to the visual cortex cannot recognize objects, but may still be able to follow and orient toward moving stimuli, although more slowly than usual. If one half of the SC is removed, however, the cats will circle constantly toward the side of the lesion, and orient compulsively toward objects located there, but fail to orient at all toward objects located in the opposite hemifield. These deficits diminish over time but never disappear.

Eye movements
In primates, eye movements can be divided into several types: fixation, in which the eyes are directed toward a motionless object, with eye movements only to compensate for movements of the head; smooth pursuit, in which the eyes move steadily to track a moving object; saccades, in which the eyes move very rapidly from one location to another; and vergence, in which the eyes move simultaneously in opposite directions to obtain or maintain single binocular vision. The superior colliculus is involved in all of these, but its role in saccades has been studied most intensively.[21][22][23]

Each of the two colliculi — one on each side of the brain — contains a two-dimensional map representing half of the visual field. The fovea — the region of maximum sensitivity — is represented at the front edge of the map, and the periphery at the back edge. Eye movements are evoked by activity in the deep layers of the SC. During fixation, neurons near the front edge — the foveal zone — are tonically active. During smooth pursuit, neurons a small distance from the front edge are activated, leading to small eye movements. For saccades, neurons are activated in a region that represents the point to which the saccade will be directed. Just prior to a saccade, activity rapidly builds up at the target location and decreases in other parts of the SC. The coding is rather broad, so that for any given saccade the activity profile forms a "hill" that encompasses a substantial fraction of the collicular map: The location of the peak of this "hill" represents the saccade target.[24]

The SC encodes the target of a gaze shift, but it does not seem to specify the precise movements needed to get there.[25] The decomposition of a gaze shift into head and eye movements and the precise trajectory of the eye during a saccade depend on integration of collicular and non-collicular signals by downstream motor areas, in ways that are not yet well understood. Regardless of how the movement is evoked or performed, the SC encodes it in "retinotopic" coordinates: that is, the location of the SC 'hill" corresponds to a fixed location on the retina. This seems to contradict the observation that stimulation of a single point on the SC can result in different gaze shift directions, depending on initial eye orientation. However, it has been shown that this is because the retinal location of a stimulus is a non-linear function of target location, eye orientation, and the spherical geometry of the eye.[26]

There has been some controversy about whether the SC merely commands eye movements, and leaves the execution to other structures, or whether it actively participates in the performance of a saccade. In 1991, Munoz et al., on the basis of data they collected, argued that, during a saccade, the "hill" of activity in the SC moves gradually, to reflect the changing offset of the eye from the target location while the saccade is progressing.[27] At present, the predominant view is that, although the "hill" does shift slightly during a saccade, it does not shift in the steady and proportionate way that the "moving hill" hypothesis predicts.[28] However, moving hills may play another role in the superior colliculus; more recent experiments have demonstrated a continuously moving hill of visual memory activity when the eyes move slowly while a separate saccade target is retained.[29]

The output from the motor sector of the SC goes to a set of midbrain and brainstem nuclei, which transform the "place" code used by the SC into the "rate" code used by oculomotor neurons. Eye movements are generated by six muscles, arranged in three orthogonally-aligned pairs. Thus, at the level of the final common path, eye movements are encoded in essentially a Cartesian coordinate system.

Although the SC receives a strong input directly from the retina, in primates it is largely under the control of the cerebral cortex, which contains several areas that are involved in determining eye movements.[30] The frontal eye fields, a portion of the motor cortex, are involved in triggering intentional saccades, and an adjoining area, the supplementary eye fields, are involved in organizing groups of saccades into sequences. The parietal eye fields, farther back in the brain, are involved mainly in reflexive saccades, made in response to changes in the view. Recent evidence[31][32] suggests that the primary visual cortex (V1) guides reflexive eye movements, according to V1 Saliency Hypothesis, using a bottom-up saliency map of the visual field generated in V1 from external visual inputs.[33]

The SC only receives visual inputs in its superficial layers, whereas the deeper layers of the colliculus receive also auditory and somatosensory inputs and are connected to many sensorimotor areas of the brain. The colliculus as a whole is thought to help orient the head and eyes toward something seen and heard.[8][34][35][36]

The superior colliculus also receives auditory information from the inferior colliculus. This auditory information is integrated with the visual information already present to produce the ventriloquism effect.

Distractibility
As well as being related to eye movements, the SC appears to have an important role to play in the circuitry underpinning distractibility. Heightened distractibility occurs in normal aging [37] and is also a central feature in a number of medical conditions, including attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).[38] Research has shown that lesions to the SC in a number of species can result in heightened distractibility[39][40] and, in humans, removing the inhibitory control on the SC from the pre-frontal cortex, therefore increasing activity in the area, also increases distractibility.[41] Research in an animal model of ADHD, the spontaneously hypertensive rat, also shows altered collicular-dependent behaviours[42][43] and physiology.[43] Furthermore, amphetamine (a mainstay treatment for ADHD) also suppresses activity in the colliculus in healthy animals.[44]

Other animals
Other mammals
Primates
It is usually accepted that the primate superior colliculus is unique among mammals, in that it does not contain a complete map of the visual field seen by the contralateral eye. Instead, like the visual cortex and lateral geniculate nucleus, each colliculus represents only the contralateral half of the visual field, up to the midline, and excludes a representation of the ipsilateral half.[45] This functional characteristic is explained by the absence, in primates, of anatomical connections between the retinal ganglion cells in the temporal half of the retina and the contralateral superior colliculus. In other mammals, the retinal ganglion cells throughout the contralateral retina project to the contralateral colliculus. This distinction between primates and non-primates has been one of the key lines of evidence in support of the flying primates theory proposed by Australian neuroscientist Jack Pettigrew in 1986, after he discovered that flying foxes (megabats) resemble primates in terms of the pattern of anatomical connections between the retina and superior colliculus.[46]

Cats
In the cat the superior colliculus projects through the reticular formation and interacts with motor neurons in the brainstem.[47]

Bats
Bats are not, in fact, blind, but they depend much more on echolocation than vision for navigation and prey capture. They obtain information about the surrounding world by emitting sonar chirps and then listening for the echoes. Their brains are highly specialized for this process, and some of these specializations appear in the superior colliculus.[48] In bats, the retinal projection occupies only a thin zone just beneath the surface, but there are extensive inputs from auditory areas, and outputs to motor areas capable of orienting the ears, head, or body. Echoes coming from different directions activate neurons at different locations in the collicular layers,[49] and activation of collicular neurons influences the chirps that the bats emit. Thus, there is a strong case that the superior colliculus performs the same sorts of functions for the auditory-guided behaviors of bats that it performs for the visual-guided behaviors of other species.

Bats are usually classified into two main groups: Microchiroptera (the most numerous, and commonly found throughout the world), and Megachiroptera (fruit bats, found in Asia, Africa and Australasia). With one exception, Megabats do not echolocate, and rely on a developed sense of vision to navigate. The visual receptive fields of neurons in the superior colliculus in these animals form a precise map of the retina, similar to that found in cats and primates.

Rodents
The superior colliculus in rodents have been hypothesized to mediate sensory-guided approach and avoidance behaviors.[50][51] Studies employing circuit analysis tools on mouse superior colliculus have revealed several important functions.[12] In a series of studies, researchers have identified a set of Ying-Yang circuit modules in the superior colliculus to initiate prey capture and predator avoidance behaviors in mice.[52][53][54][55] By using single-cell RNA-sequencing, researchers have analyzed the gene expression profiles of superior colliculus neurons and identified the unique genetic markers of these circuit modules.[56]

Other vertebrates
Optic tectum


The optic tectum is the visual center in the non-mammalian brain which develops from the alar plate of the mesencephalon. In these other vertebrates the connections from the optic tectum are important for the recognition and reaction to various sized objects which is facilitated by excitatory optic nerve transmitters like L-glutamate.[58]

Disrupting visual experience early on in zebrafish development results in a change in tectal activity. Changes in tectal activity resulted in an inability to successfully hunt and capture prey.[59] Hypothalamus inhibitory signaling to the deep tectal neuropil is important in tectal processing in zebrafish larvae. The tectal neuropil contains structures including periventricular neuronal axons and dendrites. The neuropil also contains GABAergic superficial inhibitory neurons located in stratum opticum.[60] Instead of a large cerebral cortex, zebrafish have a relatively large optic tectum that is hypothesized to carry out some of the visual processing that the cortex performs in mammals.[61]

Recent lesion studies have suggested that the optic tectum has no influence over higher-order motion responses like the optomotor response or the optokinetic response,[62] but may be more integral to lower-order cues in motion perception like in the identification of small objects.[63]

The optic tectum is one of the fundamental components of the vertebrate brain, existing across a range of species.[64] Some aspects of the structure are very consistent, including a structure composed of a number of layers, with a dense input from the optic tracts to the superficial layers and another strong input conveying somatosensory input to deeper layers. Other aspects are highly variable, such as the total number of layers (from 3 in the African lungfish to 15 in the goldfish[65]), and the number of different types of cells (from 2 in the lungfish to 27 in the house sparrow[65]).

The optic tectum is closely associated with an adjoining structure called the nucleus isthmi, which has drawn a lot of interest because it evidently makes a very important contribution to tectal function.[66] (In the superior colliculus the like structure is termed the parabigeminal nucleus). The nucleus isthmii is divided into two parts, called isthmus pars magnocellularis (Imc; "the part with the large cells") and isthmus pars parvocellularis (Ipc); "the part with the small cells"). Connections between the three areas — optic tectum, Ipc, and Imc — are topographic. Neurons in the superficial layers of the optic tectum project to corresponding points in the Ipc and Imc. The projections to the Ipc are tightly focused, while the projections to the Imc are somewhat more diffuse. Ipc gives rise to tightly focused cholinergic projections both to Imc and the optic tectum. In the optic tectum, the cholinergic inputs from Ipc ramify to give rise to terminals that extend across an entire column, from top to bottom. Imc, in contrast, gives rise to GABAergic projections to Ipc and optic tectum that spread very broadly in the lateral dimensions, encompassing most of the retinotopic map. Thus, the tectum-Ipc-Imc circuit causes tectal activity to produce recurrent feedback that involves tightly focused excitation of a small column of neighboring tectal neurons, together with global inhibition of distant tectal neurons.

The optic tectum is involved in many responses including swimming in fish, flight in birds, tongue-strikes toward prey in frogs, and fang-strikes in snakes. In some species, including fish and birds, the optic tectum, also known as the optic lobe, is one of the largest components of the brain.

In hagfish, lamprey, and shark it is a relatively small structure, but in teleost fish it is greatly expanded, in some cases becoming the largest structure in the brain. In amphibians, reptiles, and especially birds it is also a very significant component.[65]

In snakes that can detect infrared radiation, such as pythons and pit vipers, the initial neural input is through the trigeminal nerve instead of the optic tract. The rest of the processing is similar to that of the visual sense and, thus, involves the optic tectum.[67]

Fish

Lamprey
The lamprey has been extensively studied because it has a relatively simple brain that is thought in many respects to reflect the brain structure of early vertebrate ancestors. Inspired by the pioneering work of Carl Rovainen that began in the 1960s (see [68]), since the 1970s Sten Grillner and his colleagues at the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm have used the lamprey as a model system to try to work out the principles of motor control in vertebrates, starting in the spinal cord and working upward into the brain.[69] In common with other systems (see [70] for a historical perspective of the idea), neural circuits within the spinal cord seem capable of generating some basic rhythmic motor patterns underlying swimming, and that these circuits are influenced by specific locomotor areas in the brainstem and midbrain, that are in turn influenced by higher brain structures including the basal ganglia and tectum. In a study of the lamprey tectum published in 2007,[71] they found that electrical stimulation could elicit eye movements, lateral bending movements, or swimming activity, and that the type, amplitude, and direction of movement varied as a function of the location within the tectum that was stimulated. These findings were interpreted as consistent with the idea that the tectum generates goal-directed locomotion in the lamprey as shown in other species.

Birds

In birds the optic tectum is involved in flight and is one of the largest brain components. The study of avian visual processing has enabled a greater understanding of that in mammals including humans.[72]

See also
Additional images
-
Scheme showing central connections of the optic nerves and optic tracts. (Superior colliculus visible near center.)
-
Superior colliculus (coronal section)
-
Brainstem. Posterior view.
Notes
- ^ a b Squire, L (2013). Fundamental neuroscience (Fourth ed.). Academic Press. p. 707. ISBN 9780123858702.
- ^ Knudsen, EI (June 2011). "Control from below: the role of a midbrain network in spatial attention". The European Journal of Neuroscience. 33 (11): 1961–72. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2011.07696.x. PMC 3111946. PMID 21645092.
- ^ Liu, Tsung-Han; Chiao, Chuan-Chin (25 January 2017). "Mosaic Organization of Body Pattern Control in the Optic Lobe of Squids". Journal of Neuroscience. 37 (4): 768–780. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0768-16.2016. PMC 6597019. PMID 28123014.
- ^ a b Basso, MA; May, PJ (15 September 2017). "Circuits for Action and Cognition: A View from the Superior Colliculus". Annual Review of Vision Science. 3: 197–226. doi:10.1146/annurev-vision-102016-061234. PMC 5752317. PMID 28617660.
- ^ Wallace et al., 1998
- ^ Gandhi et al., 2011
- ^ Lunenburger et al., 2001
- ^ a b Kustov & Robinson, 1996
- ^ Sinnatamby, Chummy S. (2011). Last's Anatomy (12th ed.). Elsevier Australia. p. 476. ISBN 978-0-7295-3752-0.
- ^ "IX. Neurology. 4b. The Mid-brain or Mesencephalon. Gray, Henry. 1918. Anatomy of the Human Body". www.bartleby.com. Retrieved 10 October 2019.
- ^ Wang, SR (2003). "The nucleus isthmi and dual modulation of the receptive field of tectal neurons in non-mammals". Brain Research Reviews. 41 (1): 13–25. doi:10.1016/s0165-0173(02)00217-5. PMID 12505645.
- ^ a b Ito, S; Feldheim, DA (2018). "The Mouse Superior Colliculus: An Emerging Model for Studying Circuit Formation and Function". Frontiers in Neural Circuits. 12: 10. doi:10.3389/fncir.2018.00010. PMC 5816945. PMID 29487505.
- ^ Huerta & Harting, 1984
- ^ Agster, Kara L.; Burwell, Rebecca D. (December 2009). "Cortical efferents of the perirhinal, postrhinal, and entorhinal cortices of the rat". Hippocampus. 19 (12): 1159–1186. doi:10.1002/hipo.20578. PMC 3066185. PMID 19360714.
- ^ Clemo HR, Stein BE (1984). "Topographic organization of somatosensory corticotectal influences in cat". Journal of Neurophysiology. 51 (5): 843–858. doi:10.1152/jn.1984.51.5.843. PMID 6726314.
- ^ a b Chavalier & Mana, 2000
- ^ a b Illing, 1996
- ^ Mana & Chevalier, 2001
- ^ Reichenthal, Adam; Ben-Tov, Mor; Segev, Ronen (2018). "Coding Schemes in the Archerfish Optic Tectum". Frontiers in Neural Circuits. 12: 18. doi:10.3389/fncir.2018.00018. PMC 5845554. PMID 29559898.
- ^ Sprague, 1996
- ^ Basso, MA; May, PJ (2017). "Circuits for Action and Cognition: A View from the Superior Colliculus". Annual Review of Vision Science. 3: 197–226. doi:10.1146/annurev-vision-102016-061234. PMC 5752317. PMID 28617660.
- ^ Furlan, M; Smith, AT; Walker, R (2015). "Activity in the human superior colliculus relating to endogenous saccade preparation and execution". Journal of Neurophysiology. 114 (2): 1048–1058. doi:10.1152/jn.00825.2014. PMC 4725108. PMID 26041830.
- ^ Moschovakis, A K (1996). "The superior colliculus and eye movement control". Current Opinion in Neurobiology. 6 (6): 811–816. doi:10.1016/s0959-4388(96)80032-8. PMID 9000018.
- ^ Soetedjo, R; Kaneko, CRS; Fuchs, AF (2002). "Evidence against a moving hill in the superior colliculus during saccadic eye movements in the monkey". Journal of Neurophysiology. 87 (6): 2778–2789. doi:10.1152/jn.2002.87.6.2778. PMID 12037180.
- ^ Sparks & Gandhi, 2003
- ^ Klier et al., 2001
- ^ Munoz et al., 1991
- ^ Soetedjo et al., 2002
- ^ Dash et al., 2015
- ^ Pierrot-Deseilligny et al., 2003
- ^ Yan, Yin; Zhaoping, Li; Li, Wu (2018-10-09). "Bottom-up saliency and top-down learning in the primary visual cortex of monkeys". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 115 (41): 10499–10504. Bibcode:2018PNAS..11510499Y. doi:10.1073/pnas.1803854115. PMC 6187116. PMID 30254154.
- ^ Zhang, Xilin; Zhaoping, Li; Zhou, Tiangang; Fang, Fang (2012-01-12). "Neural Activities in V1 Create a Bottom-Up Saliency Map". Neuron. 73 (1): 183–192. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2011.10.035. ISSN 0896-6273. PMID 22243756.
- ^ Li, Zhaoping (2002-01-01). "A saliency map in primary visual cortex". Trends in Cognitive Sciences. 6 (1): 9–16. doi:10.1016/S1364-6613(00)01817-9. ISSN 1364-6613. PMID 11849610. S2CID 13411369.
- ^ Klier et al., 2003
- ^ Krauzlis et al., 2004
- ^ Sparks, 1999
- ^ Prendergast, M. A.; Jackson, W. J.; Terry, A. V.; Kille, N. J.; Arneric, S. P.; Decker, M. W.; Buccafusco, J. J. (1998-03-01). "Age-related differences in distractibility and response to methylphenidate in monkeys". Cerebral Cortex. 8 (2): 164–172. doi:10.1093/cercor/8.2.164. ISSN 1047-3211. PMID 9542895.
- ^ Douglas, V (1983). Developmental neuropsychiatry. New York: Guildford Press. pp. 280–329.
- ^ Goodale, M. A.; Foreman, N. P.; Milner, A. D. (1978-03-01). "Visual orientation in the rat: A dissociation of deficits following cortical and collicular lesions". Experimental Brain Research. 31 (3): 445–457. doi:10.1007/BF00237301. ISSN 0014-4819. PMID 648607. S2CID 41871236.
- ^ Milner, A. D.; Foreman, N. P.; Goodale, M. A. (1978-01-01). "Go-left go-right discrimination performance and distractibility following lesions of prefrontal cortex or superior colliculus in stumptail macaques". Neuropsychologia. 16 (4): 381–390. doi:10.1016/0028-3932(78)90062-3. PMID 99682. S2CID 35425621.
- ^ Gaymard, Bertrand; François, Chantal; Ploner, Christoph J.; Condy, Carine; Rivaud-Péchoux, Sophie (2003-04-01). "A direct prefrontotectal tract against distractibility in the human brain". Annals of Neurology. 53 (4): 542–545. doi:10.1002/ana.10560. ISSN 1531-8249. PMID 12666125. S2CID 40340479.
- ^ Dommett, Eleanor J.; Rostron, Claire L. (2011-11-01). "Abnormal air righting behaviour in the spontaneously hypertensive rat model of ADHD". Experimental Brain Research. 215 (1): 45–52. doi:10.1007/s00221-011-2869-7. ISSN 0014-4819. PMID 21931982. S2CID 18981985.
- ^ a b Brace, L.R.; Kraev, I.; Rostron, C.L.; Stewart, M.G; Overton, P.G.; Dommett, E.J. (2015). "Altered visual processing in a rodent model of Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder". Neuroscience. 303: 364–377. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.07.003. PMID 26166731. S2CID 38148654.
- ^ Clements, K.M.; Devonshire, I.M.; Reynolds, J.N.J.; Overton, P.G. (2014). "Enhanced visual responses in the superior colliculus in an animal model of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder and their suppression by d-amphetamine". Neuroscience. 274: 289–298. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.05.054. PMID 24905438. S2CID 38787839.
- ^ Lane et al., 1973
- ^ Pettigrew, 1986
- ^ Precht, W. (1974). "Tectal influences on cat ocular motoneurons". Brain Research. 20 (1): 27–40. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(74)90890-7. PMID 4373140.
- ^ Ulanovsky & Moss, 2008
- ^ Valentine & Moss, 1997
- ^ Westby, G. W. M.; Keay, K. A.; Redgrave, P.; Dean, P.; Bannister, M. (August 1990). "Output pathways from the rat superior colliculus mediating approach and avoidance have different sensory properties". Experimental Brain Research. 81 (3): 626–638. doi:10.1007/BF02423513. PMID 2226694. S2CID 22140043.
- ^ Cohen, J. D.; Castro-Alamancos, M. A. (23 June 2010). "Neural Correlates of Active Avoidance Behavior in Superior Colliculus". Journal of Neuroscience. 30 (25): 8502–8511. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1497-10.2010. PMC 2905738. PMID 20573897.
- ^ Shang, Congping; Liu, Zhihui; Chen, Zijun; Shi, Yingchao; Wang, Qian; Liu, Su; Li, Dapeng; Cao, Peng (2015-06-26). "A parvalbumin-positive excitatory visual pathway to trigger fear responses in mice". Science. 348 (6242): 1472–1477. Bibcode:2015Sci...348.1472S. doi:10.1126/science.aaa8694. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 26113723. S2CID 40701489.
- ^ Shang, Congping; Chen, Zijun; Liu, Aixue; Li, Yang; Zhang, Jiajing; Qu, Baole; Yan, Fei; Zhang, Yaning; Liu, Weixiu; Liu, Zhihui; Guo, Xiaofei (December 2018). "Divergent midbrain circuits orchestrate escape and freezing responses to looming stimuli in mice". Nature Communications. 9 (1): 1232. Bibcode:2018NatCo...9.1232S. doi:10.1038/s41467-018-03580-7. ISSN 2041-1723. PMC 5964329. PMID 29581428.
- ^ Shang, Congping; Liu, Aixue; Li, Dapeng; Xie, Zhiyong; Chen, Zijun; Huang, Meizhu; Li, Yang; Wang, Yi; Shen, Wei L.; Cao, Peng (June 2019). "A subcortical excitatory circuit for sensory-triggered predatory hunting in mice". Nature Neuroscience. 22 (6): 909–920. doi:10.1038/s41593-019-0405-4. ISSN 1097-6256. PMID 31127260. S2CID 163165114.
- ^ Huang, Meizhu; Li, Dapeng; Cheng, Xinyu; Pei, Qing; Xie, Zhiyong; Gu, Huating; Zhang, Xuerong; Chen, Zijun; Liu, Aixue; Wang, Yi; Sun, Fangmiao (December 2021). "The tectonigral pathway regulates appetitive locomotion in predatory hunting in mice". Nature Communications. 12 (1): 4409. Bibcode:2021NatCo..12.4409H. doi:10.1038/s41467-021-24696-3. ISSN 2041-1723. PMC 8292483. PMID 34285209.
- ^ Xie, Zhiyong; Wang, Mengdi; Liu, Zeyuan; Shang, Congping; Zhang, Changjiang; Sun, Le; Gu, Huating; Ran, Gengxin; Pei, Qing; Ma, Qiang; Huang, Meizhu (2021-07-28). "Transcriptomic encoding of sensorimotor transformation in the midbrain". eLife. 10: e69825. doi:10.7554/eLife.69825. ISSN 2050-084X. PMC 8341986. PMID 34318750.
- ^ Caltharp SA, Pira CU, Mishima N, Youngdale EN, McNeill DS, Liwnicz BH, Oberg KC (2007). "NOGO-A induction and localization during chick brain development indicate a role disparate from neurite outgrowth inhibition". BMC Dev. Biol. 7 (1): 32. doi:10.1186/1471-213X-7-32. PMC 1865376. PMID 17433109.
- ^ Beart, Phillip (1976). "An evaluation of L-glutamate as the transmitter released from optic nerve terminals of the pigeon". Brain Research. 110 (1): 99–114. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(76)90211-0. PMID 6128. S2CID 24316801.
- ^ Avitan, L.; Pujic, Z.; Mölter, J.; Van De Poll, M.; Sun, B.; Teng, H.; Amor, R.; Scott, E.K.; Goodhill, G.J. (2017). "Spontaneous Activity in the Zebrafish Tectum Reorganizes over Development and Is Influenced by Visual Experience". Current Biology. 27 (16): 2407–2419. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2017.06.056. PMID 28781054.
- ^ Dunn, Timothy W; et al. (2016). "Neural Circuits Underlying Visually Evoked Escapes in Larval Zebrafish". Neuron. 89 (3): 613–28. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2015.12.021. PMC 4742414. PMID 26804997.
- ^ Heap, LA; Vanwalleghem, GC; Thompson, AW; Favre-Bulle, I; Rubinsztein-Dunlop, H; Scott, EK (2018). "Hypothalamic Projections to the Optic Tectum in Larval Zebrafish". Front Neuroanat. 11: 135. doi:10.3389/fnana.2017.00135. PMC 5777135. PMID 29403362.
- ^ Roeser, Tobias (2003). "Visuomotor Behaviors in Larval Zebrafish after GFP-Guided Laser Ablation of the Optic Tectum". Journal of Neuroscience. 23 (9): 3726–3734. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-09-03726.2003. PMC 6742205. PMID 12736343.
- ^ Barker, Alison (2015). "Sensorimotor Decision Making in the Zebrafish Tectum". Current Biology. 25 (21): 2804–2814. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2015.09.055. PMID 26592341.
- ^ Maximino, 2008
- ^ a b c Northcutt, 2002
- ^ Henriques, Pedro M.; Rahman, Niloy; Jackson, Samuel E.; Bianco, Isaac H. (3 June 2019). "Nucleus Isthmi Is Required to Sustain Target Pursuit during Visually Guided Prey-Catching". Current Biology. 29 (11): 1771–1786.e5. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2019.04.064. PMC 6557330. PMID 31104935.
- ^ Hartline et al., 1978
- ^ Rovainen C (1979) Neurobiology of lampreys. Physiological reviews 59:1007-1077.
- ^ Grillner, 2003
- ^ Stuart D, Hultborn H (2008) Thomas Graham Brown (1882--1965), Anders Lundberg (1920-), and the neural control of stepping. Brain Res Rev 59:74-95.
- ^ Saitoh et al., 2007
- ^ Wylie, DR; Gutierrez-Ibanez, C; Pakan, JM; Iwaniuk, AN (December 2009). "The optic tectum of birds: mapping our way to understanding visual processing". Canadian Journal of Experimental Psychology. 63 (4): 328–38. doi:10.1037/a0016826. PMID 20025392. S2CID 2712427.
References
- Chevalier, G; Mana S (2000). "Honeycomb-like structure of the intermediate layers of the rat superior colliculus, with additional observations in several other mammals: AChE patterning". J Comp Neurol. 419 (2): 137–53. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1096-9861(20000403)419:2<137::AID-CNE1>3.0.CO;2-6. PMID 10722995. S2CID 26050145.
- Dash, S; Yang X; Wang H; Crawford JD (2015). "Continuous updating of visuospatial memory in superior colliculus during slow eye movements". Curr Biol. 25 (3): 267–74. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2014.11.064. PMID 25601549.
- Dean, P; Redgrave P; Westby GW (1989). "Event or emergency? Two response systems in the mammalian superior colliculus". Trends Neurosci. 12 (4): 137–47. doi:10.1016/0166-2236(89)90052-0. PMID 2470171. S2CID 25268593.
- Gandhi, NJ; Katani HA (2011). "Motor Functions of the Superior Colliculus". Annu Rev Neurosci. 34: 205–231. doi:10.1146/annurev-neuro-061010-113728. PMC 3641825. PMID 21456962.
- Grillner, S (2003). "The motor infrastructure: from ion channels to neuronal networks". Nature Reviews Neuroscience. 4 (7): 573–86. doi:10.1038/nrn1137. PMID 12838332. S2CID 4303607.
- Hartline, PH; Kass L; Loop MS (1978). "Merging of modalities in the optic tectum: infrared and visual integration in rattlesnakes". Science. 199 (4334): 1225–9. Bibcode:1978Sci...199.1225H. doi:10.1126/science.628839. PMID 628839.
- Huerta, MF; Harting JK (1984). Vanegas H (ed.). Comparative Neurology of the Optic Tectum. New York: Plenum Press. pp. 687–773. ISBN 978-0-306-41236-3.
- Illing, R-B (1996). "Chapter 2 the mosaic architecture of the superior colliculus". Extrageniculostriate Mechanisms Underlying Visually-Guided Orientation Behavior. Progress in Brain Research. Vol. 112. pp. 17–34. doi:10.1016/S0079-6123(08)63318-X. ISBN 9780444823472. PMID 8979818.
{{cite book}}:|journal=ignored (help) - King, AJ; Schnupp JWH; Carlile S; Smith AL; Thompson ID (1996). "Chapter 24 the development of topographically-aligned maps of visual and auditory space in the superior colliculus". Extrageniculostriate Mechanisms Underlying Visually-Guided Orientation Behavior. Progress in Brain Research. Vol. 112. pp. 335–350. doi:10.1016/S0079-6123(08)63340-3. ISBN 9780444823472. PMID 8979840.
{{cite book}}:|journal=ignored (help) - Klier, EM; Wang H; Crawford JD (2001). "The superior colliculus encodes gaze commands in retinal coordinates" (PDF). Nat Neurosci. 4 (6): 627–32. doi:10.1038/88450. PMID 11369944. S2CID 4930662.
- Klier, E; Wang H; Crawford D (2003). "Three-dimensional eye-head coordination is implemented downstream from the superior colliculus". J Neurophysiol. 89 (5): 2839–53. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.548.1312. doi:10.1152/jn.00763.2002. PMID 12740415.
- Krauzlis, R; Liston D; Carello C (2004). "Target selection and the superior colliculus: goals, choices and hypotheses". Vision Res. 44 (12): 1445–51. doi:10.1016/j.visres.2004.01.005. PMID 15066403. S2CID 5705421.
- Kustov, A; Robinson D (1996). "Shared neural control of attentional shifts and eye movements". Nature. 384 (6604): 74–77. Bibcode:1996Natur.384...74K. doi:10.1038/384074a0. PMID 8900281. S2CID 68917.
- Lane, RH; Allman JM; Kaas JH; Miezin FM (1973). "The visuotopic organization of the superior colliculus of the owl monkey (Aotus trivirgatus) and the bush baby (Galago senegalensis)". Brain Res. 60 (2): 335–49. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(73)90794-4. PMID 4202853.
- Lunenburger, L; Kleiser R; Stuphorn V; Miller LE; Hoffmann KP (2001). "Chapter 8 a possible role of the superior colliculus in eye-hand coordination". Vision: From Neurons to Cognition. Progress in Brain Research. Vol. 134. pp. 109–25. doi:10.1016/S0079-6123(01)34009-8. ISBN 9780444505866. PMID 11702538.
{{cite book}}:|journal=ignored (help) - Mana, S; Chevalier G (2001). "Honeycomb-like structure of the intermediate layers of the rat superior colliculus: afferent and efferent connections". Neuroscience. 103 (3): 673–93. doi:10.1016/S0306-4522(01)00026-4. PMID 11274787. S2CID 45660874.
- Maximino, C; Soares, Daphne (2008). Soares, Daphne (ed.). "Evolutionary changes in the complexity of the tectum of nontetrapods: a cladistic approach". PLOS ONE. 3 (10): e385. Bibcode:2008PLoSO...3.3582M. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0003582. PMC 2571994. PMID 18974789.
- Munoz, DP; Pélisson D; Guitton D (1991). "Movement of activity on the superior colliculus motor map during gaze shifts" (PDF). Science. 251 (4999): 1358–60. doi:10.1126/science.2003221. PMID 2003221.
- Northcutt, RG (2002). "Understanding vertebrate brain evolution". Integr Comp Biol. 42 (4): 743–6. doi:10.1093/icb/42.4.743. PMID 21708771.
- Pettigrew, JD (1986). "Flying primates? Megabats have the advanced pathway from eye to midbrain". Science. 231 (4743): 1304–6. Bibcode:1986Sci...231.1304P. doi:10.1126/science.3945827. PMID 3945827. S2CID 16582493.
- Pierrot-Deseilligny, C; Müri RM; Ploner CJ; Gaymard B; Rivaud-Péchoux S (2003). "Cortical control of ocular saccades in humans: A model for motricity". Neural Control of Space Coding and Action Production. Progress in Brain Research. Vol. 142. pp. 3–17. doi:10.1016/S0079-6123(03)42003-7. ISBN 9780444509772. PMID 12693251.
{{cite book}}:|journal=ignored (help) - Saitoh, K; Ménard A; Grillner S (2007). "Tectal control of locomotion, steering, and eye movements in lamprey". J Neurophysiol. 97 (4): 3093–108. doi:10.1152/jn.00639.2006. PMID 17303814. S2CID 5711513.
- Soetedjo, R; Kaneko CR; Fuchs AF (2002). "Evidence against a moving hill in the superior colliculus during saccadic eye movements in the monkey". J Neurophysiol. 87 (6): 2778–89. doi:10.1152/jn.2002.87.6.2778. PMID 12037180. S2CID 18294502.
- Sparks, DL (1999). "Conceptual issues related to the role of the superior colliculus in the control of gaze". Current Opinion in Neurobiology. 9 (6): 698–707. doi:10.1016/S0959-4388(99)00039-2. PMID 10607648. S2CID 14389002.
- Sparks, DL; Gandhi NJ (2003). "Single cell signals: An oculomotor perspective". Neural Control of Space Coding and Action Production. Progress in Brain Research. Vol. 142. pp. 35–53. doi:10.1016/S0079-6123(03)42005-0. ISBN 9780444509772. PMID 12693253.
{{cite book}}:|journal=ignored (help) - Sprague, JM (1996). "Chapter 1 Neural mechanisms of visual orienting responses". Extrageniculostriate Mechanisms Underlying Visually-Guided Orientation Behavior. Progress in Brain Research. Vol. 112. pp. 1–15. doi:10.1016/S0079-6123(08)63317-8. ISBN 9780444823472. PMID 8979817.
{{cite book}}:|journal=ignored (help) - Stein, BE; Clamman HP (1981). "Control of pinna movements and sensorimotor register in cat superior colliculus". Brain Behav Evol. 19 (3–4): 180–192. doi:10.1159/000121641. PMID 7326575.
- Ulanovsky, N; Moss CF (2008). "What the bat's voice tells the bat's brain". PNAS. 105 (25): 8491–98. Bibcode:2008PNAS..105.8491U. doi:10.1073/pnas.0703550105. PMC 2438418. PMID 18562301.
- Valentine, D; Moss CF (1997). "Spatially selective auditory responses in the superior colliculus of the echolocating bat". J Neurosci. 17 (5): 1720–33. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-05-01720.1997. PMC 6573370. PMID 9030631.
- Wallace, MT; Meredith MA; Stein BE (1998). "Multisensory integration in the superior colliculus of the alert cat". J Neurophysiol. 80 (2): 1006–10. doi:10.1152/jn.1998.80.2.1006. PMID 9705489.
External links
See what we do next...
OR
By submitting your email or phone number, you're giving mschf permission to send you email and/or recurring marketing texts. Data rates may apply. Text stop to cancel, help for help.
Success: You're subscribed now !



